



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询








参考图片
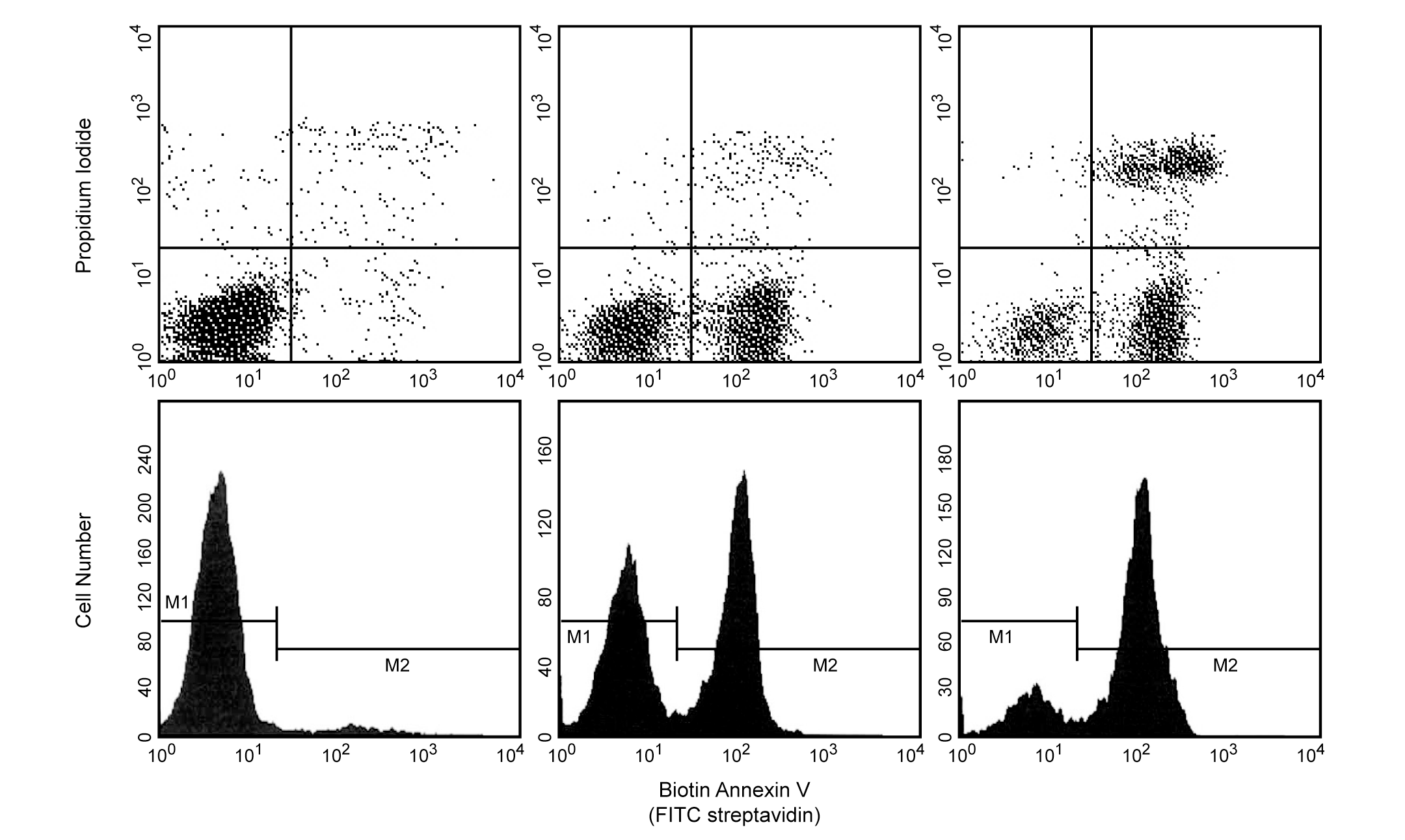
Biotin Annexin V: A tool for identifying cells that are undergoing apoptosis. Jurkat T cells were left untreated (upper left & lower left panels), treated for 5 hours (upper middle & lower middle panels) or 12 hours (upper right & lower right panels) with anti-human Fas antibody (clone DX2, Cat. No. 555670) and Protein G. Cells were incubated with Biotin Annexin V, followed by incubation with SAv-FITC in a buffer containing Propidium Iodide (PI). Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry. Untreated cells were primarily Biotin Annexin V and PI negative, indicating that they were viable and not undergoing apoptosis. After a 5 hr treatment with DX2, there were two populations of cells: cells undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V positive and PI negative), and cells that were viable and not undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V and PI negative). After a 12 hr treatment with DX2, three populations of cells were identified: cells that had already died or were in late stage of apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V and PI positive), cells undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V positive and PI negative), and cells that were viable and not undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V and PI negative). The addition of Protein G enhances the ability of DX2 to induce apoptosis, presumably by cross-linking the Fas receptor.
Biotin Annexin V: A tool for identifying cells that are undergoing apoptosis. Jurkat T cells were left untreated (upper left & lower left panels), treated for 5 hours (upper middle & lower middle panels) or 12 hours (upper right & lower right panels) with anti-human Fas antibody (clone DX2, Cat. No. 555670) and Protein G. Cells were incubated with Biotin Annexin V, followed by incubation with SAv-FITC in a buffer containing Propidium Iodide (PI). Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry. Untreated cells were primarily Biotin Annexin V and PI negative, indicating that they were viable and not undergoing apoptosis. After a 5 hr treatment with DX2, there were two populations of cells: Cells undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V positive and PI negative), and cells that were viable and not undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V and PI negative). After a 12 hr treatment with DX2, three populations of cells were identified: Cells that had already died or were in late stage of apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V and PI positive), cells undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V positive and PI negative), and cells that were viable and not undergoing apoptosis (Biotin Annexin V and PI negative). The addition of Protein G enhances the ability of DX2 to induce apoptosis, presumably by cross-linking the Fas receptor.





 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)