


 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询
Lys19-His317 (C130R), with C-terminal 8*His Tag KVEQAVETEPEPELRQQTEWQSGQRWELALGRFWDYLRWVQTLSEQVQEELLSSQVTQELRALMDETMKELKAYKSELEEQLTPVAEETRARLSKELQAAQARLGADMEDVRGRLVQYRGEVQAMLGQSTEELRVRLASHLRKLRKRLLRDADDLQKRLAVYQAGAREGAERGLSAIRERLGPLVEQGRVRAATVGSLAGQPLQERAQAWGERLRARMEEMGSRTRDRLDEVKEQVAEVRAKLEEQAQQIRLQAEAFQARLKSWFEPLVEDMQRQWAGLVEKVQAAVGTSAAPVPSDNHGGGSHHHHHHHH









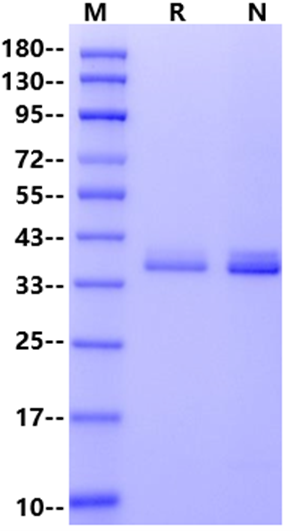
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing\ncondition).
"}]

Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a lipid carrier in both the peripheral and the central nervous systems. Lipid-loaded apoE lipoprotein particles bind to several cell surface receptors to support membrane homeostasis and injury repair in the brain. Considering prevalence and relative risk magnitude, the ε4 allele of the APOE gene is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). ApoE4 contributes to AD pathogenesis by modulating multiple pathways, including but not limited to the metabolism, aggregation, and toxicity of amyloid-β peptide, tauopathy, synaptic plasticity, lipid transport, glucose metabolism, mitochondrial function, vascular integrity, and neuroinflammation.


12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied; 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution; 1 week, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution; Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
1. Na Zhao, Chia-Chen Liu, Wenhui Qiao. Apolipoprotein E, Receptors, and Modulation of Alzheimer's Disease. Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 15;83(4):347-357. Epub 2017 Mar 14.

参考图片
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
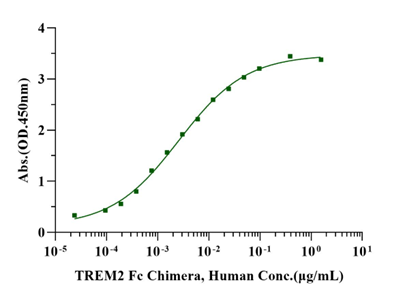
Immobilized Apolipoprotein E/APOE4 His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA030062) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind TREM2 Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010593) with EC50 of 2.08-3.22ng/ml.





 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)