


1/2

品牌: BD Pharmingen
 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询反应种属:
Mouse (QC Testing)
Mouse (QC Testing)
来源宿主:
Rat LOU, also known as Louvain, LOU/C, LOU/M IgG2a, κ
Rat LOU, also known as Louvain, LOU/C, LOU/M IgG2a, κ
产品介绍
产品信息
耦联标记
BUV737

抗原名称
CD8a

宿主
Rat LOU, also known as Louvain, LOU/C, LOU/M IgG2a, κ

免疫原
Mouse Spleen Cells or Thymocyte Membranes

简单描述
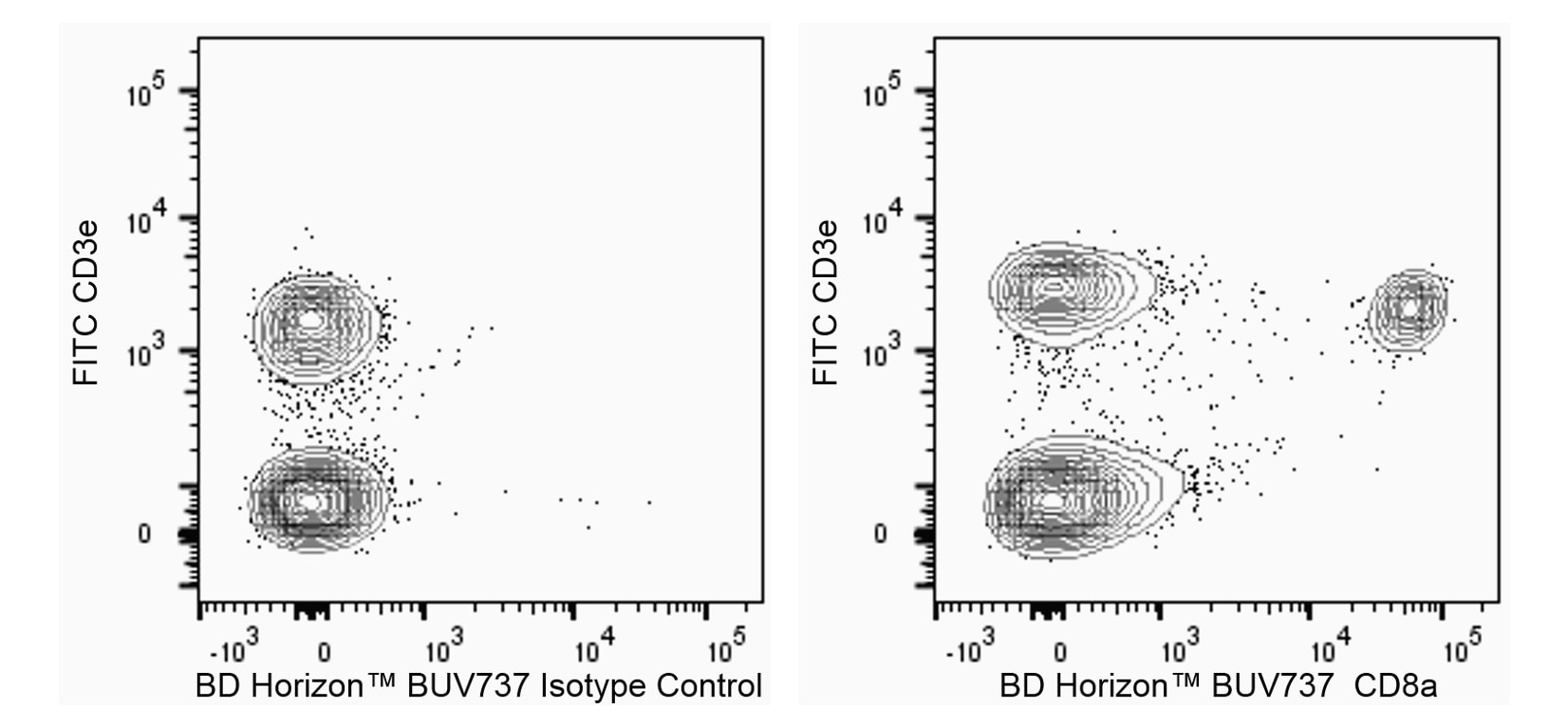
The 53-6.7 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the 38 kDa α and 34 kDa α' chains of the CD8 differentiation antigen (Ly-2 or Lyt-2) of all mouse strains tested. The CD8 α and α' chains (CD8a) form heterodimers with the CD8 β chain (CD8b, Ly-3, or Lyt-3) on the surface of most thymocytes. A subpopulation of mature T lymphocytes (i.e., MHC class I-restricted T cells, including most T suppressor/cytotoxic cells) expresses almost exclusively the CD8 αβ heterodimer. Subsets of γδ TCR-bearing T cells, intestinal intrapithelial lymphocytes, and dendritic cells express CD8a without CD8b. It has been suggested that the expression of the CD8a/CD8b heterodimer is restricted to T lymphocytes which matured in the thymus or in an extrathymic environment that had been influenced by thymus-initiated neuroendocrine signals. CD8 is an antigen coreceptor on the T-cell surface which interacts with MHC class I molecules on antigen-presenting cells or epithelial cells. It participates in T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck (p56 [lck]). The CD8 α and α' chains arise from alternatively spliced messengers of a single CD8a gene. The longer α form associates with p56 [lck] via a CXCP motif in its cytoplasmic domain, which it shares with CD4, but not with CD8b. The truncated α' chain is unable to associate with p56 [lck], and it may function to attenuate the CD8-mediated costimulatory signal during intrathymic T-cell maturation. In vivo and in vitro treatment with 53-6.7 mAb has reportedly been effective at depleting CD8+ peripheral T lymphocytes. The 53-6.7 antibody has also been reported to cross-react with CD8 α- and α'-like polypeptides on subsets of thymic and peripheral lymphocytes in the Egyptian toad, Bufo regularis.
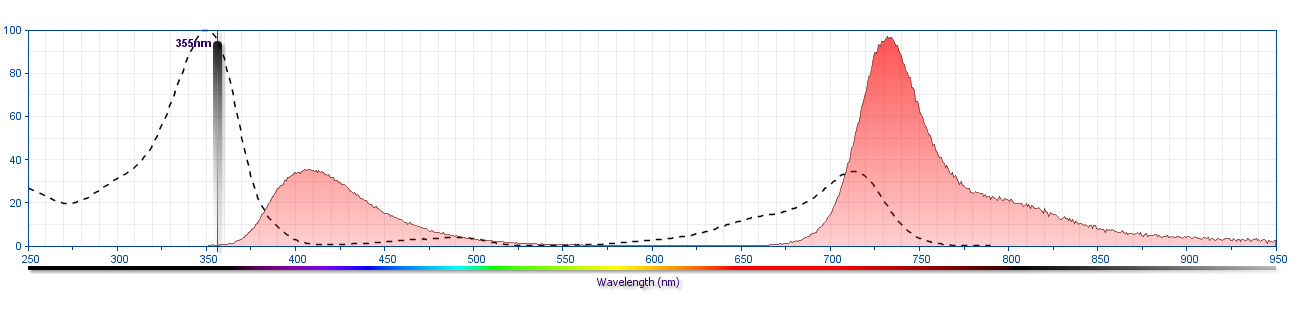
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BUV737 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome with an Ex Max near 350 nm and an Em Max near 737 nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV737 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 740/35 nm filter. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by the red laser line, there may be significant spillover into red laser detectors with filters in the 700-720 nm range.

商品描述
The 53-6.7 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the 38 kDa α and 34 kDa α" chains of the CD8 differentiation antigen (Ly-2 or Lyt-2) of all mouse strains tested. The CD8 α and α" chains (CD8a) form heterodimers with the CD8 β chain (CD8b, Ly-3, or Lyt-3) on the surface of most thymocytes. A subpopulation of mature T lymphocytes (i.e., MHC class I-restricted T cells, including most T suppressor/cytotoxic cells) expresses almost exclusively the CD8 αβ heterodimer. Subsets of γδ TCR-bearing T cells, intestinal intrapithelial lymphocytes, and dendritic cells express CD8a without CD8b. It has been suggested that the expression of the CD8a/CD8b heterodimer is restricted to T lymphocytes which matured in the thymus or in an extrathymic environment that had been influenced by thymus-initiated neuroendocrine signals. CD8 is an antigen coreceptor on the T-cell surface which interacts with MHC class I molecules on antigen-presenting cells or epithelial cells. It participates in T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck (p56 [lck]). The CD8 α and α" chains arise from alternatively spliced messengers of a single CD8a gene. The longer α form associates with p56 [lck] via a CXCP motif in its cytoplasmic domain, which it shares with CD4, but not with CD8b. The truncated α" chain is unable to associate with p56 [lck], and it may function to attenuate the CD8-mediated costimulatory signal during intrathymic T-cell maturation. In vivo and in vitro treatment with 53-6.7 mAb has reportedly been effective at depleting CD8+ peripheral T lymphocytes. The 53-6.7 antibody has also been reported to cross-react with CD8 α- and α"-like polypeptides on subsets of thymic and peripheral lymphocytes in the Egyptian toad, Bufo regularis.
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BUV737 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome with an Ex Max near 350 nm and an Em Max near 737 nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV737 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 740/35 nm filter. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by the red laser line, there may be significant spillover into red laser detectors with filters in the 700-720 nm range.

产品详情
BUV737
The BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet 737 (BUV737) Dye is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This tandem fluorochrome is comprised of a BUV395 donor with an excitation maximum (Ex Max) of 350-nm and an acceptor dye with an emission maximum (Em Max) at 735-nm. BUV737, driven by BD innovation, is designed to be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355-nm) and detected using an optical filter centered near 740-nm (e.g., 740/35 bandpass filter). The acceptor dye can be excited by the Red (628–640nm) laser resulting in cross-laser excitation and fluorescence spillover. Please ensure that your instrument’s configurations (lasers and optical filters) are appropriate for this dye.
BUV737
Ultraviolet 355 nm
350 nm
735 nm
应用
反应种属
Mouse (QC Testing)

背景
别名
KIR2DL1 (CD158a/NKAT-1); KIR2DS1 (CD158h); KIR2DS3 (NKAT-7); KIR2DS5 (CD158g/NKAT-9)

制备和贮存
存储溶液
Aqueous buffered solution containing ≤0.09% sodium azide.

保存方式
Aqueous buffered solution containing ≤0.09% sodium azide.
文献
文献
研发参考(14)
1. Fujiura Y, Kawaguchi M, Kondo Y, et al. Development of CD8 alpha alpha+ intestinal intraepithelial T cells in beta 2-microglobulin- and/or TAP1-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1996; 156(8):2710-2715. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry).
2. Hathcock KS. T cell depletion by cytotoxic elimination. Curr Protoc Immunol. 1991; 1:3.4.1-3.4.3. (Clone-specific: Cell separation, Depletion, Flow cytometry).
3. Kruisbeek AM, Shevach EM. Proliferative assays for T cell function. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004; 3:3.12.1-3.12.14. (Clone-specific: Depletion, In vivo exacerbation).
4. LeFrancois L. Extrathymic differentiation of intraepithelial lymphocytes: generation of a separate and unequal T-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1991; 12(12):436-438. (Biology).
5. Ledbetter JA, Herzenberg LA. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979; 47:63-90. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation).
6. Ledbetter JA, Rouse RV, Micklem HS, Herzenberg LA. T cell subsets defined by expression of Lyt-1,2,3 and Thy-1 antigens. Two-parameter immunofluorescence and cytotoxicity analysis with monoclonal antibodies modifies current views. J Exp Med. 1980; 152(2):280-295. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry).
7. Ledbetter JA, Seaman WE, Tsu TT, Herzenberg LA. Lyt-2 and lyt-3 antigens are on two different polypeptide subunits linked by disulfide bonds. Relationship of subunits to T cell cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1981; 153(6):1503-1516. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation, Inhibition).
8. Leishman AJ, Naidenko OV, Attinger A, et al. T cell responses modulated through interaction between CD8alphaalpha and the nonclassical MHC class I molecule, TL. Science. 2001; 294(5548):1848-1849. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry).
9. MacDonald HR, Schreyer M, Howe RC, Bron C. Selective expression of CD8 alpha (Ly-2) subunit on activated thymic gamma/delta cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990; 20(4):927-930. (Biology).
10. Nakayama K, Nakayama K, Negishi I, et al. Requirement for CD8 beta chain in positive selection of CD8-lineage T cells. Science. 1994; 263(5150):1131-1133. (Biology).
11. Sydora BC, Brossay L, Hagenbaugh A, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H. TAP-independent selection of CD8+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1996; 156(11):4209-4216. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry).
12. Takahashi K, Nakata M, Tanaka T, et al. CD4 and CD8 regulate interleukin 2 responses of T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89(12):5557-5561. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation, Inhibition).
13. Vremec D, Zorbas M, Scollay R, et al. The surface phenotype of dendritic cells purified from mouse thymus and spleen: investigation of the CD8 expression by a subpopulation of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1992; 176(1):47-58. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry).
14. van Ewijk W, van Soest PL, van den Engh GJ. Fluorescence analysis and anatomic distribution of mouse T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies to the antigens Thy-1, Lyt-1, Lyt-2, and T-200. J Immunol. 1981; 127(6):2594-2604. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry).

数据库链接
Entrez-Gene ID
12525

声明 :本官网所有报价均为常温或者蓝冰运输价格,如有产品需要干冰运输,需另外加收干冰运输费。





 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)