
 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询



Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:50 |





Specificity/Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey






参考图片
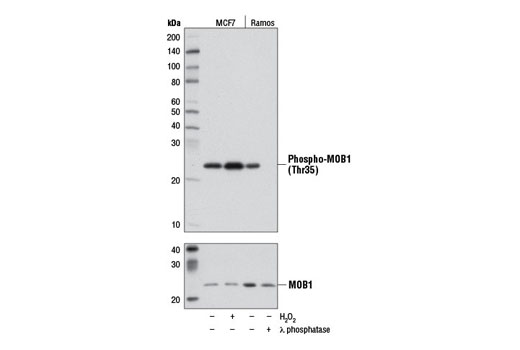
Western blot analysis of extracts from MCF7 cells, either untreated (-) or treated (+) with H2O2 (2.5 mM, 30 min) and Ramos cells, either untreated (-) or treated (+) with λ phosphatase, using Phospho-MOB1 (Thr35) (D2F10) Rabbit mAb (upper) and MOB1 Antibody #3863 (lower).
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma using Phospho-MOB1 (Thr35) (D2F10) Rabbit mAb.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human ovarian carcinoma control (left) or lambda phosphatase-treated (right) using Phospho-MOB1 (Thr35) (D2F10) Rabbit mAb.
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded MCF7 cell pellets, control (left) or H2O2-treated (right), using Phospho-MOB1 (Thr35) (D2F10) Rabbit mAb.






 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)