


 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
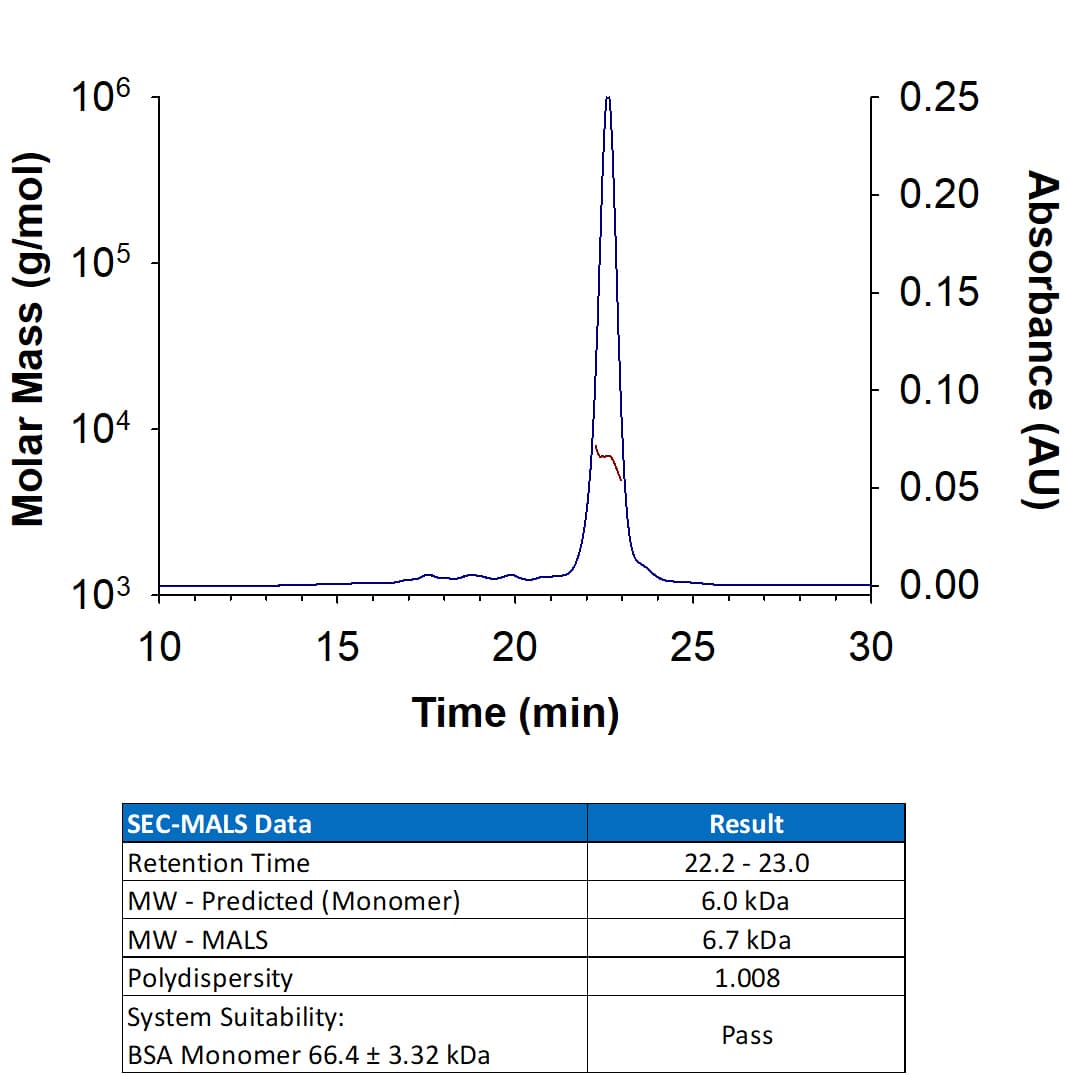
View LargerRecombinant Human EGF Protein (Catalog # 236-EG) has a molecular weight (MW) of 6.7 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a monomer.
 View Larger
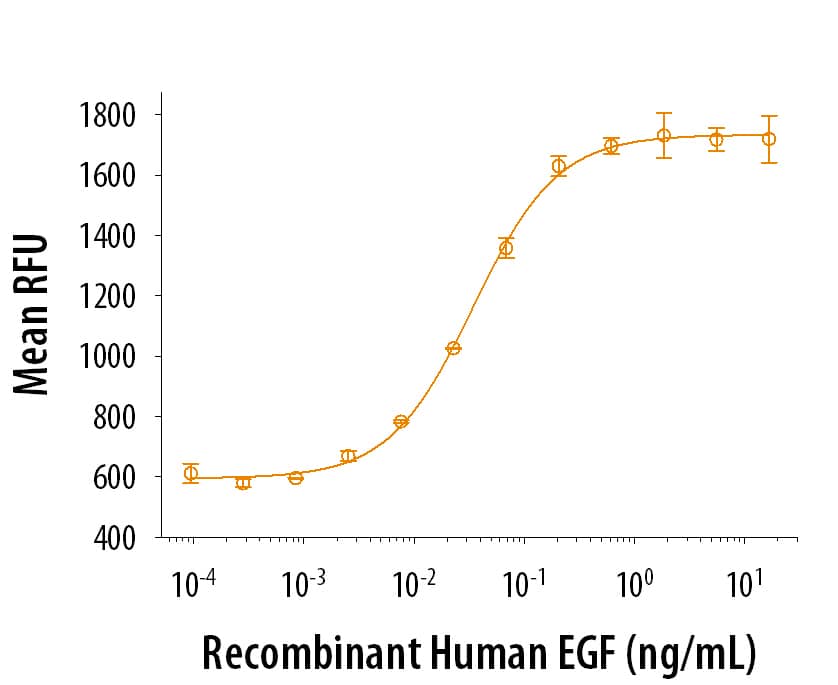
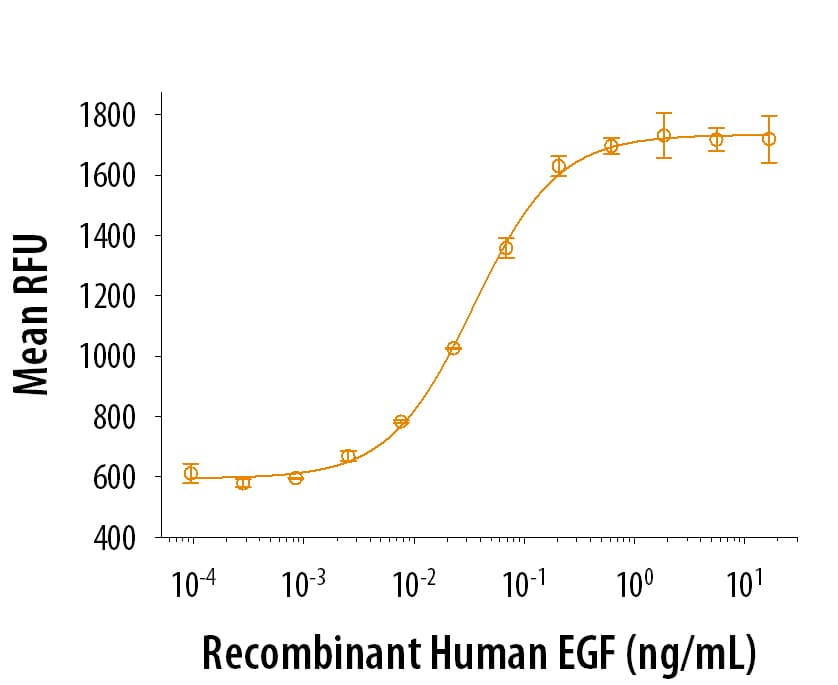
View LargerRecombinant Human EGF (Catalog # 236‑EG) stimulates cell proliferation of the Balb/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 20‑100 pg/mL.
 View Larger
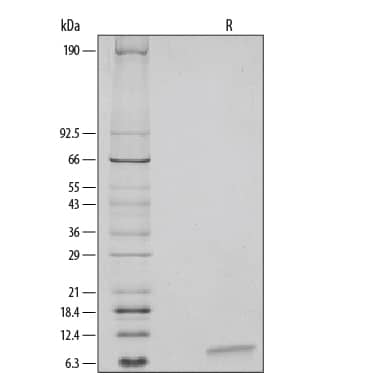
View Larger1 µg/lane of Recombinant Human EGF was resolved with SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining under reducing (R) conditions, showing a single band at 6 kDa.
 View Larger
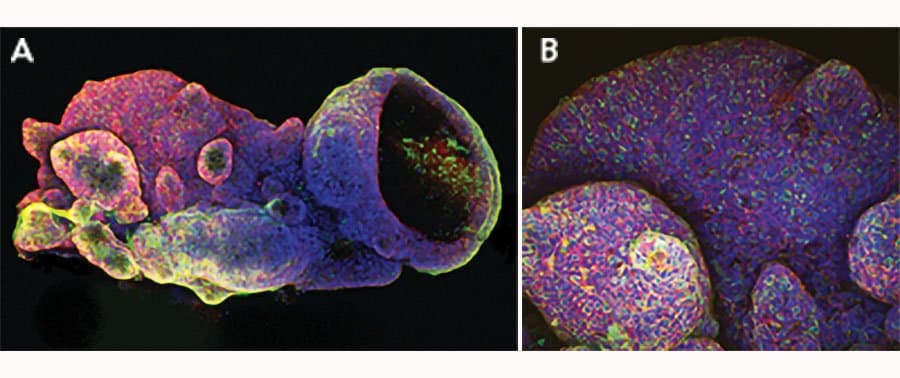
View LargeriPSC-derived human intestinal organoids were cultured using Cultrex™ UltiMatrix RGF Basement Membrane Extract (BME001-05) and intestinal organoid culture medium, which includes Recombinant Human EGF (Catalog # 236-EG), Recombinant Human Noggin (6057-NG), Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 (4645-RS), and Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (5036-WN), along with the other reagents listed in the intestinal organoid culture medium recipe in the human intestinal organoid culture protocol. (A) Human intestinal organoids were stained using a Rat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat Vimentin Monoclonal Antibody (MAB2105; green) and a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Desmin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (AF3844; red) to visualize myofibroblast cells and counterstained with DAPI (5748; blue). (B) Human intestinal organoids were stained using a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (AF748; green) and a Mouse Anti-Human MUC2 Monoclonal Antibody (Novus Biologicals, Catalog # NBP2-44431; red) and counterstained with DAPI (5748; blue).
 View Larger
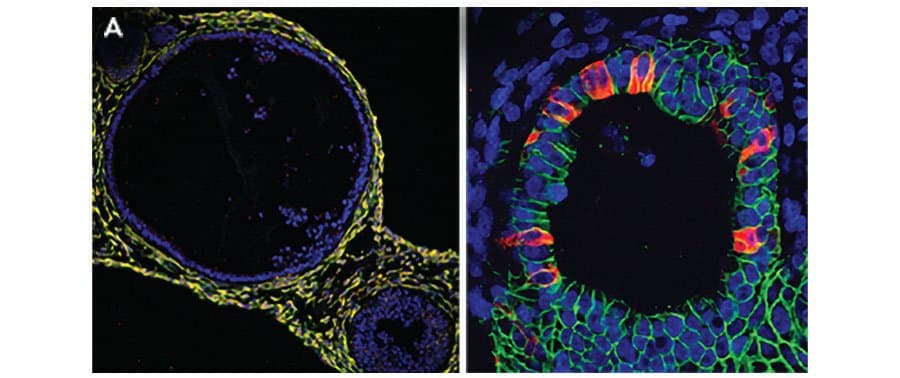
View LargerAdult stem cells isolated from human descending colon were embedded in Cultrex UltiMatrix RGF Basement Membrane Extract (BME001-05) and cultured for 30 days in intestinal organoid culture medium, which includes Recombinant Human EGF (Catalog # 236-EG), Recombinant Human Noggin (6057-NG), Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 (4645-RS), and Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (5036-WN), along with the other reagents listed in the intestinal organoid culture medium recipe in the human intestinal organoid culture protocol. (A) Organoids were fixed and stained with a Mouse Anti-Human MUC2 Monoclonal Antibody (Novus Biologicals; Catalog # NBP2-44431; green) to visualize intestinal goblet cells and counterstained with a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (AF748; red) and DAPI (5748; blue). The image shown was taken at 10x magnification. (B) Organoids were fixed and stained with a Mouse Anti-Human Chromogranin A Monoclonal Antibody (MAB90981; green) to visualize enteroendocrine cells and counterstained with a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (AF748; red) and DAPI (5748; blue). The image shown was taken at 20x magnification.
 View Larger
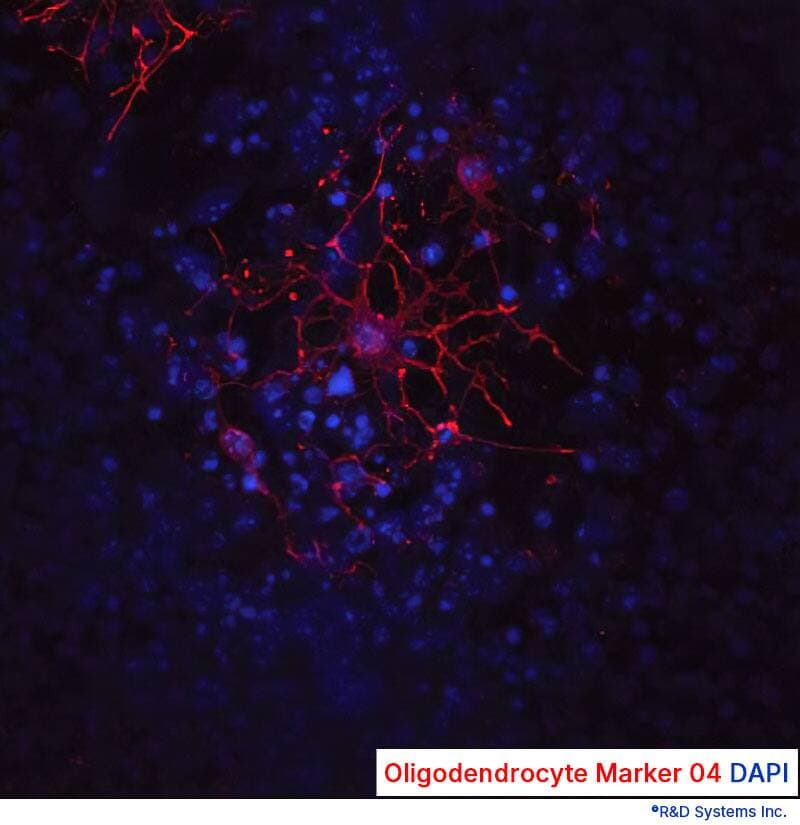
View LargerD3 mouse embryonic stem cells were expanded in KO-ES Media supplemented with Bovine Fibronectin Protein (1030-FN) to support cell attachment and spreading, the ITS and N-2 Plus Media Supplements (AR013 and AR003), and a panel of growth factors for effective oligodendrocyte differentiation, including Recombinant Human FGF-basic, Recombinant Human EGF (Catalog # 236-EG), and Recombinant Human PDGF-AA (221-AA). Oligodendrocytes were detected using a Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat/Chicken Oligodendrocyte Marker O4 Monoclonal Antibody (MAB1326). The cells were stained with the NorthernLights™-557 Affinity-purified Goat Anti-Mouse IgM Secondary Antibody (NL019; red). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (5748;blue).
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
236-EG
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Human EGF Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Asn971-Arg1023, with an N-terminal Met
Analysis

Background: EGF
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a small, potent growth factor capable of inducing cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. EGF is the founding member of the EGF family that also includes TGF-alpha, amphiregulin (AR), betacellulin (BTC), epiregulin (EPR), heparin‑binding EGF‑like growth factor (HB‑EGF), epigen, and the neuregulins (NRG)-1 through -6 (1). Members of The EGF family are characterized by a shared structural motif, the EGF‑like domain, which contains three intramolecular disulfide bonds that are formed by six similarly spaced, conserved cysteine residues (2). These disulfide bonds are essential for proper protein conformation and receptor binding. All EGF family members are synthesized as type I transmembrane precursor proteins that may contain several EGF domains in the extracellular region. The mature proteins are released from the cell surface by regulated proteolysis (1). The full length EGF protein is 1207 amino acids (aa) (EGF precursor) containing nine EGF domains and nine LDLR class B repeats. However, the mature protein is much smaller, only 53 aa, and is generated by proteolytic cleavage of the EGF domain proximal to the transmembrane region (3). EGF is well conserved across mammals with mature human EGF 70% identical to mature mouse and rat EGF. Physiologically, EGF is found in various body fluids, including blood, milk, urine, saliva, seminal fluid, pancreatic juice, cerebrospinal fluid, and amniotic fluid (4). EGF is a high affinity ligand of the EGF receptor (ErbB). Four ErbB (HER) family receptor tyrosine kinases including EGFR/ErbB1, ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4, mediate responses to EGF family members (5). EGF binding induces dimerization of the EGF receptor resulting in activation of the protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. These receptors undergo a complex pattern of ligand-induced homo- or hetero-dimerization to transduce EGF family signals (6, 7). EGF binds ErbB1 and depending on the context, induces the formation of homodimers or heterodimers containing ErbB2. Dimerization results in autophosphorylation of the receptor at specific tyrosine residues to create docking sites for a variety of signaling molecules (5, 8). Biological activities ascribed to EGF include epithelial development, angiogenesis, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, fibroblast proliferation, and colony formation of epidermal cells in culture.
- Harris, R.C. et al. (2003) Exp. Cell Res. 284:2.
- Carpenter, G. and Cohen, S. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265:7709.
- Bell, G.I. et al. (1986) Nucl. Acids Res. 14:8427.
- Carpenter, G. and Zendegui, J.G. (1986) Exp. Cell Res. 164:1.
- Jorissen, R.N. et al. (2003) Exp. Cell Res. 284:31.
- Gamett, D.C. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:12052.
- Qian, X. et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91:1500.
- Qian, X. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:574.


参考图片
1 µg/lane of Recombinant Human EGF was resolved with SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining under reducing (R) conditions, showing a single band at 6 kDa.
Recombinant Human EGF (Catalog # 236‑EG) stimulates cell proliferation of the Balb/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line. The ED50 for this effect is typically 20‑100 pg/mL.






 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)