


 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询












Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a member of the pro-inflammatory cytokine family, induces the expression of a variety of proteins responsible for acute inflammation, and plays an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of cells in humans. Interleukin 6 was originally identified as a T cell-derived lymphokine that induces final maturation of B cells into antibody-producing cells. Recombinant human IL-6 acts on B cells activated with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I or pokeweed mitogen (PWM) to induce immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG and IgA production, but not on resting B cells. Anti-IL-6 antibody was found to inhibit PWM-induced Ig production, indicating that IL-6 is one of the essential factors in PWM-induced Ig production. Furthermore, IL-6 was shown to augment the primary and secondary anti-SRBC (sheep red blood cell) antibody production in mice in vivo.


· 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
1、Heinrich P C. et al. (2003). Principles of interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J. 374: 1-20.
2、Rose-John S. et al. (2007) The IL-6/sIL-6R complex as a novel target for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11(5): 613-624.
3、Dinh W. et al. (2009) Elevated plasma levels of TNF-alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with diastolic dysfunction and glucose metabolism disorders. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 8:58.

参考图片
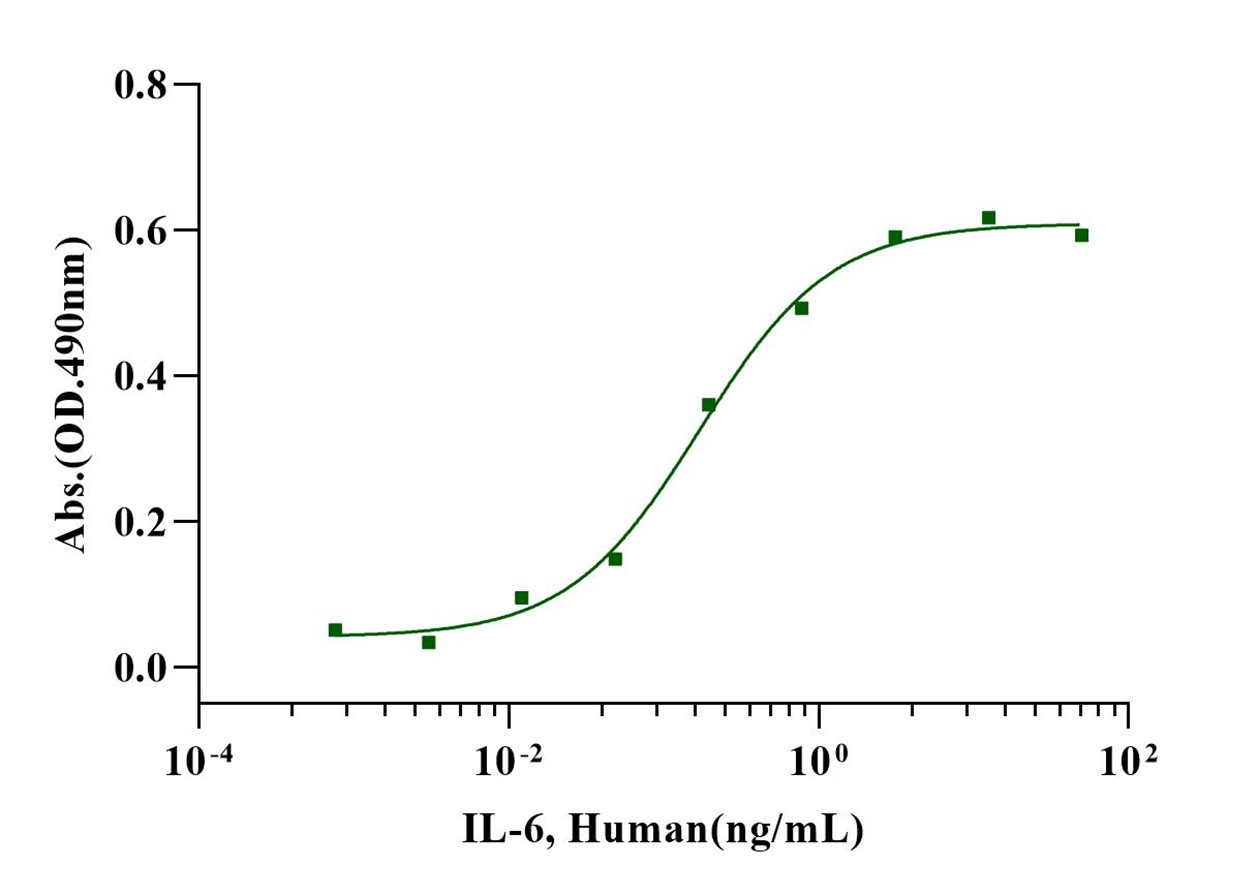
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 cells, the EC50 for this effect is less than 0.2ng/ml.
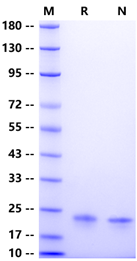
1μg (R:reducingcondition;N:non-reducingcondition).
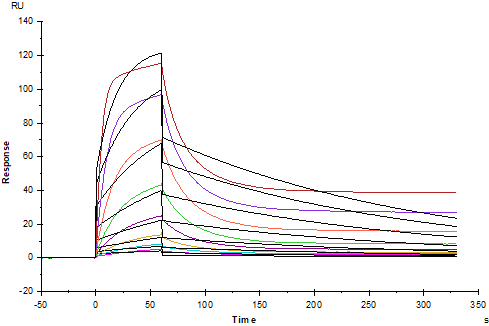
Protein A Chip captured IL-6R alpha/CD126 Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010448), can bind IL-6, Human (Cat. No. UA040052) with an affinity constant of 8.51nM as determined in SPR assay.




 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)