


 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Flow Cytometry(2.5 µg/106 cells)
Immunohistochemistry(5-15 µg/mL)
Flow Cytometry(2.5 µg/106 cells)
Immunohistochemistry(5-15 µg/mL)



Glu18-Lys590
Accession # Q08481

Scientific Data
 View Larger
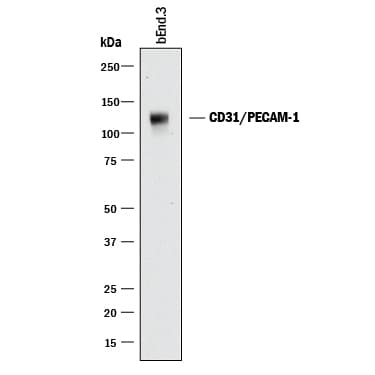
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM‑1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). A specific band was detected for CD31/PECAM-1 at approximately 130 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
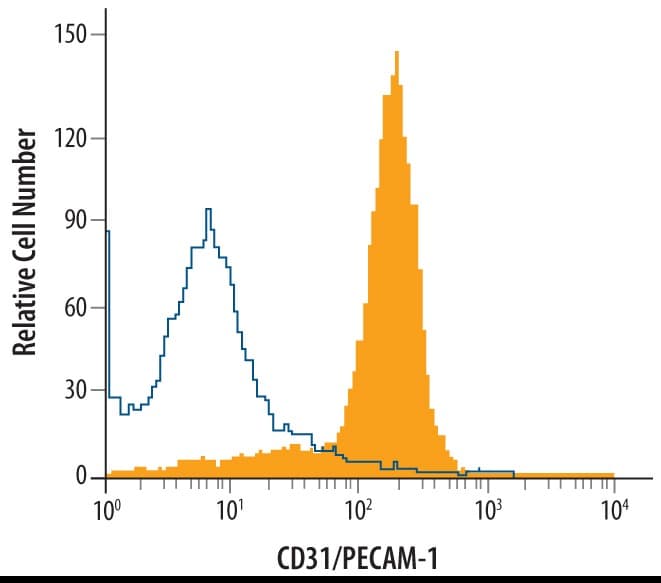
View LargerDetection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Mouse splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628, filled histogram) or control antibody (AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (F0108).
 View Larger
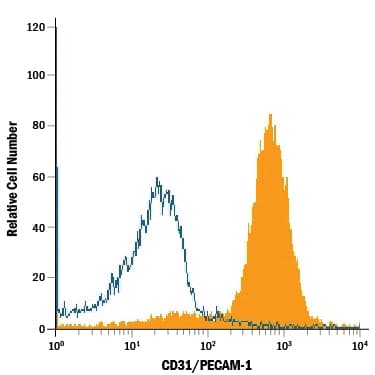
View LargerDetection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Rat Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Rat splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (F0108).
 View Larger
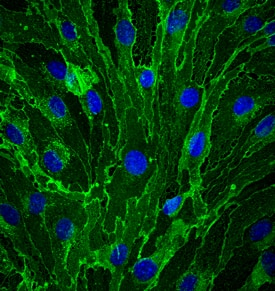
View LargerCD31/PECAM‑1 in bEnd.3 Mouse Cell Line. CD31/PECAM-1 was detected in immersion fixed bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 493-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (green; NL003) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membrane. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
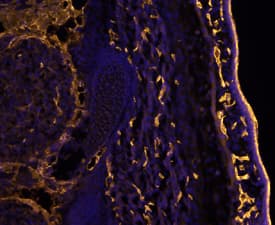
View LargerCD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Embryo. CD31/PECAM-1 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (E13.5) using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (yellow; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to developing endothelium. View our protocol for Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View LargerCD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Embryo. CD31/PECAM-1 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (14 d.p.c.) using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) at 10 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC004). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to developing guts. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
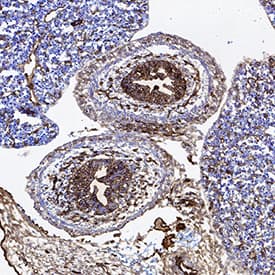
View LargerCD31/PECAM‑1 in Rat Heart. CD31/PECAM‑1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of rat heart using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) at 3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to endothelial cells in vasculature.
 View Larger
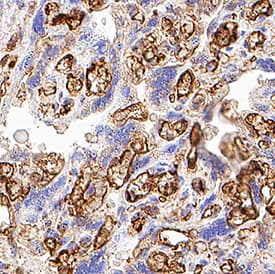
View LargerDetection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Human Placenta. CD31/PECAM‑1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Placenta using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) at 15 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using VisUCyte Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # VCTS021). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to endothelial cells in chorionic villi. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
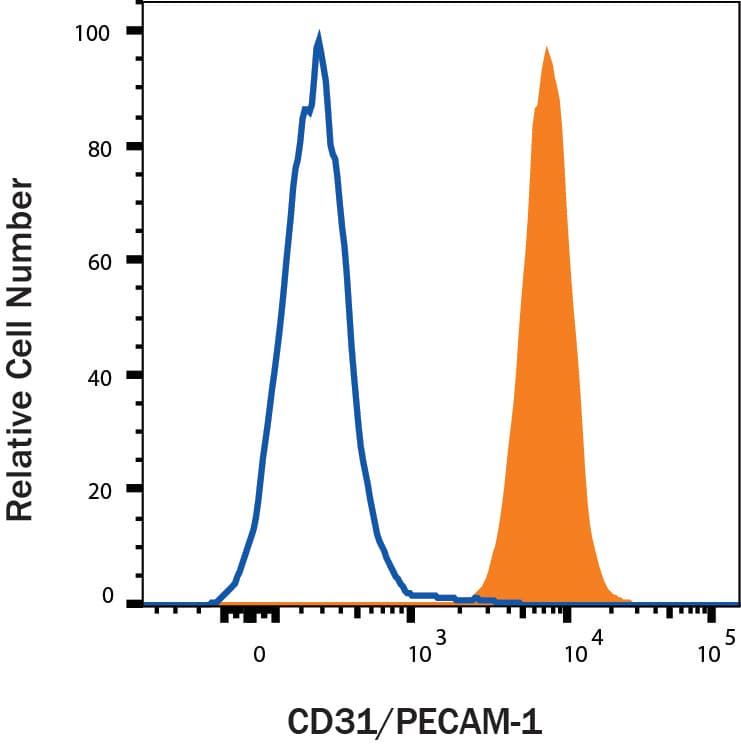
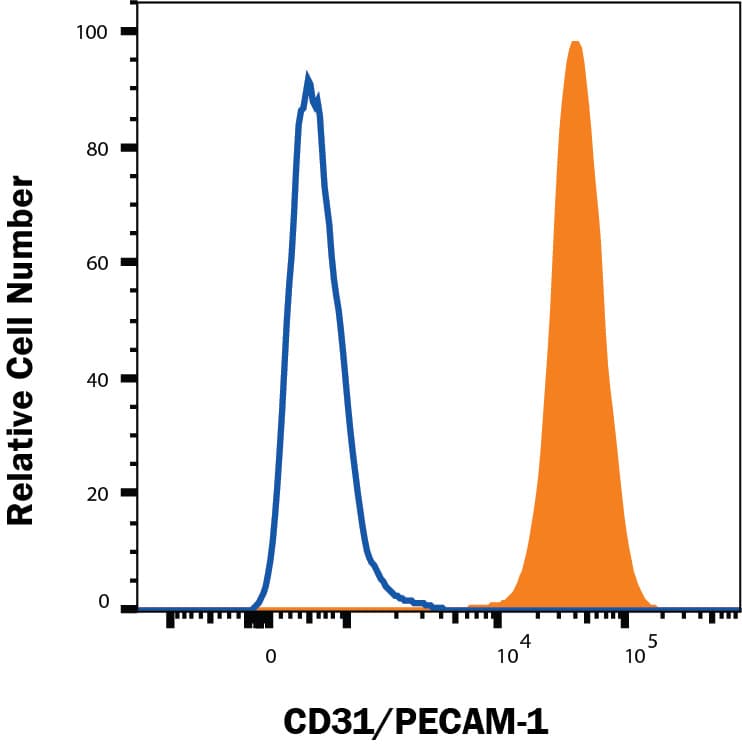
View LargerDetection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in HUVEC cells by Flow Cytometry. HUVEC cells were stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0107). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
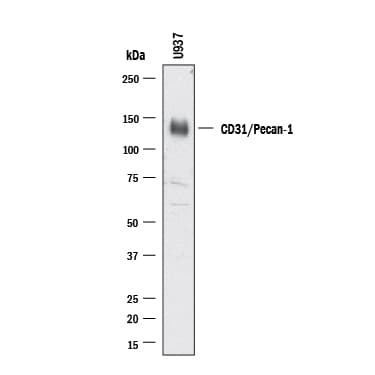
View LargerDetection of Human CD31/PECAM‑1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/ml of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (AF3628) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for CD31/PECAM‑1 at approximately 130 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
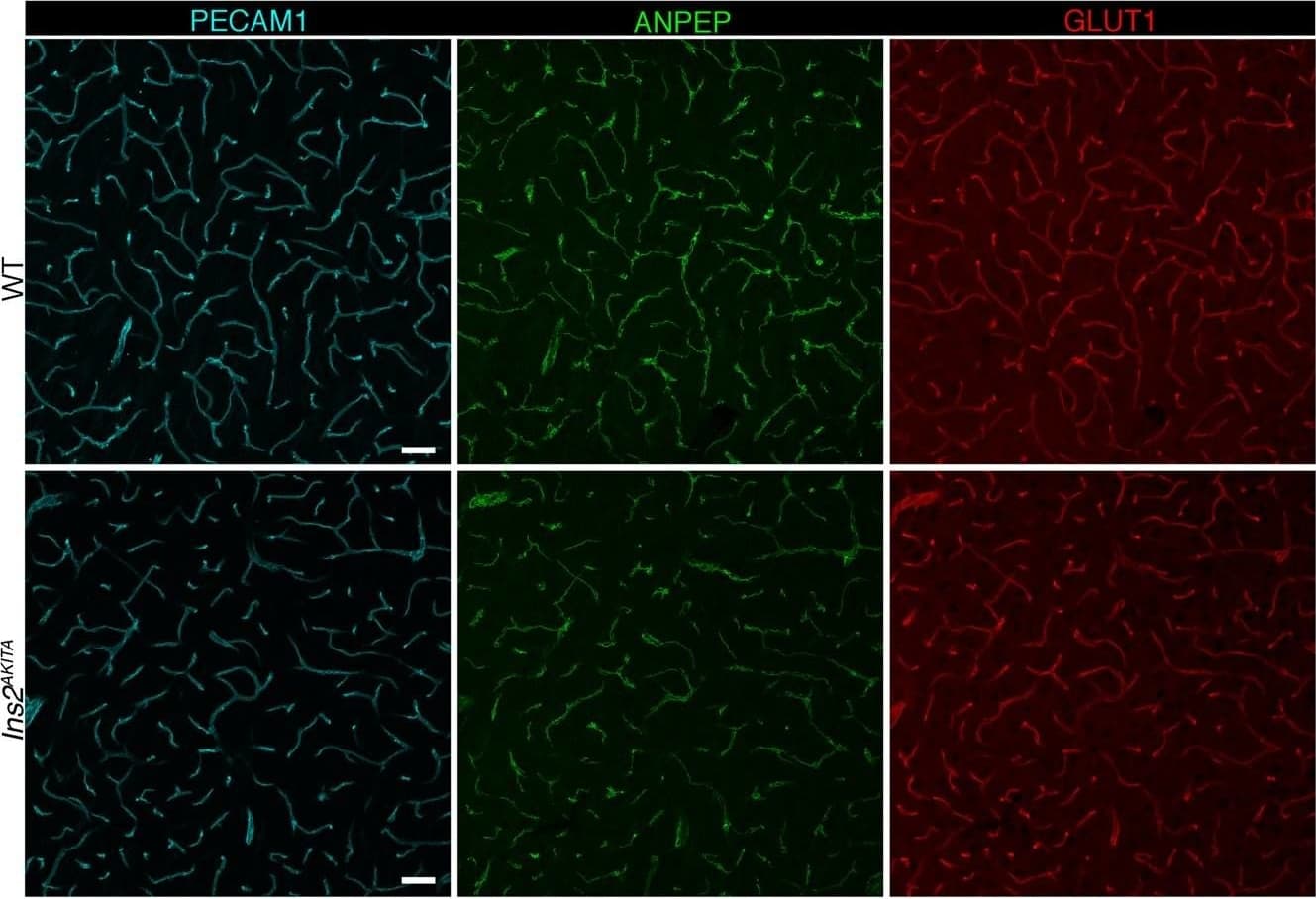
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunohistochemistry Representative image of immunostaining corresponding to the glucose transporter protein SLC2A1 (GLUT1) in 30 week-old Ins2AKITA and WT cerebral cortex. Mural cells (ANPEP, green), glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1, red), endothelium (PECAM1, cyan). n = 2, scale bar 50 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30498224), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
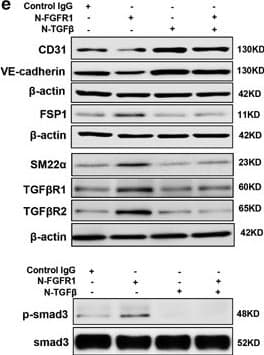
View LargerDetection of Human CD31/PECAM-1 by Western Blot AcSDKP suppresses TGF beta /smad signaling and EndMT through the FGFR1/FRS2 pathway. (a) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h, and the FGFR1, TGF beta R1 and TGF beta R2 protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (b) HMVECs were treated with TGF beta 2 in the presence or absence of N-FGFR1 for 15 min with or without AcSDKP preincubation. The p-smad3 and TGF beta R1 protein levels were analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of the p-smad3/smad3 and TGF beta R1/ beta -actin levels (n=3) in each group was performed. (c) HMVECs were incubated with either N-FGFR1 in the presence or absence of TGF beta 2 for 48 h with or without preincubation with AcSDKP for 2 h or with N-FGFR1 in the presence or absence of TGF beta 2 for 48 h with or without 24 h of incubation with FGF2 (50 ng/ml). The CD31, SM22 alpha, FSP1 and alpha -SMA protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (d) HMVECs were transfected with FRS2 siRNA (100 nM) for 48 h with or without AcSDKP preincubation. The VE-cadherin, FSP1, vimentin, SM22 alpha and p-smad3 levels were analyzed by western blot. (e) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h or 15 min in the presence or absence of N-TGF beta (1, 2, 3) (1.0 μg/ml). The CD31, VE-cadherin, SM22 alpha, FSP1, TGF beta R1, TGF beta R2 and p-smad3 levels were analyzed by western blot Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28771231), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
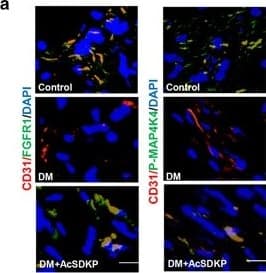
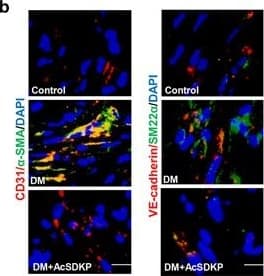
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence AcSDKP inhibits TGF beta /smad signaling and EndMT and restores the FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 levels in diabetic hearts. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/FGFR1 and CD31/P-MAP4K4 in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 μm in each panel. The CD31 and FGFR1 double-labeled cells and the CD31 and P-MAP4K4 double-labeled cells in each visual field were assessed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. (b and c) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/ alpha -SMA, VE-cadherin /SM22 alpha and CD31/p-smad3 expression levels in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 μm in each panel. The CD31 and alpha -SMA double-labeled cells, the VE-cadherin and SM22 alpha double-labeled cells and the CD31 and p-smad3 double-labeled cells in each visual field were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. Four mice from each group were analyzed. (d) Western blot analysis of the FGFR1, P-MAP4K4, TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2 and TGF beta 3 levels in cardiac tissues. A representative blot from four independent experiments was shown. The densitometric analysis of western blot data was presented (n=4). The diabetic mice are abbreviated as DM in the figure Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28771231), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
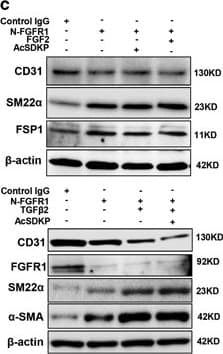
View LargerDetection of Human CD31/PECAM-1 by Western Blot AcSDKP suppresses TGF beta /smad signaling and EndMT through the FGFR1/FRS2 pathway. (a) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h, and the FGFR1, TGF beta R1 and TGF beta R2 protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (b) HMVECs were treated with TGF beta 2 in the presence or absence of N-FGFR1 for 15 min with or without AcSDKP preincubation. The p-smad3 and TGF beta R1 protein levels were analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of the p-smad3/smad3 and TGF beta R1/ beta -actin levels (n=3) in each group was performed. (c) HMVECs were incubated with either N-FGFR1 in the presence or absence of TGF beta 2 for 48 h with or without preincubation with AcSDKP for 2 h or with N-FGFR1 in the presence or absence of TGF beta 2 for 48 h with or without 24 h of incubation with FGF2 (50 ng/ml). The CD31, SM22 alpha, FSP1 and alpha -SMA protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (d) HMVECs were transfected with FRS2 siRNA (100 nM) for 48 h with or without AcSDKP preincubation. The VE-cadherin, FSP1, vimentin, SM22 alpha and p-smad3 levels were analyzed by western blot. (e) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h or 15 min in the presence or absence of N-TGF beta (1, 2, 3) (1.0 μg/ml). The CD31, VE-cadherin, SM22 alpha, FSP1, TGF beta R1, TGF beta R2 and p-smad3 levels were analyzed by western blot Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28771231), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
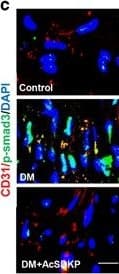
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence AcSDKP inhibits TGF beta /smad signaling and EndMT and restores the FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 levels in diabetic hearts. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/FGFR1 and CD31/P-MAP4K4 in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 μm in each panel. The CD31 and FGFR1 double-labeled cells and the CD31 and P-MAP4K4 double-labeled cells in each visual field were assessed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. (b and c) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/ alpha -SMA, VE-cadherin /SM22 alpha and CD31/p-smad3 expression levels in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 μm in each panel. The CD31 and alpha -SMA double-labeled cells, the VE-cadherin and SM22 alpha double-labeled cells and the CD31 and p-smad3 double-labeled cells in each visual field were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. Four mice from each group were analyzed. (d) Western blot analysis of the FGFR1, P-MAP4K4, TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2 and TGF beta 3 levels in cardiac tissues. A representative blot from four independent experiments was shown. The densitometric analysis of western blot data was presented (n=4). The diabetic mice are abbreviated as DM in the figure Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28771231), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
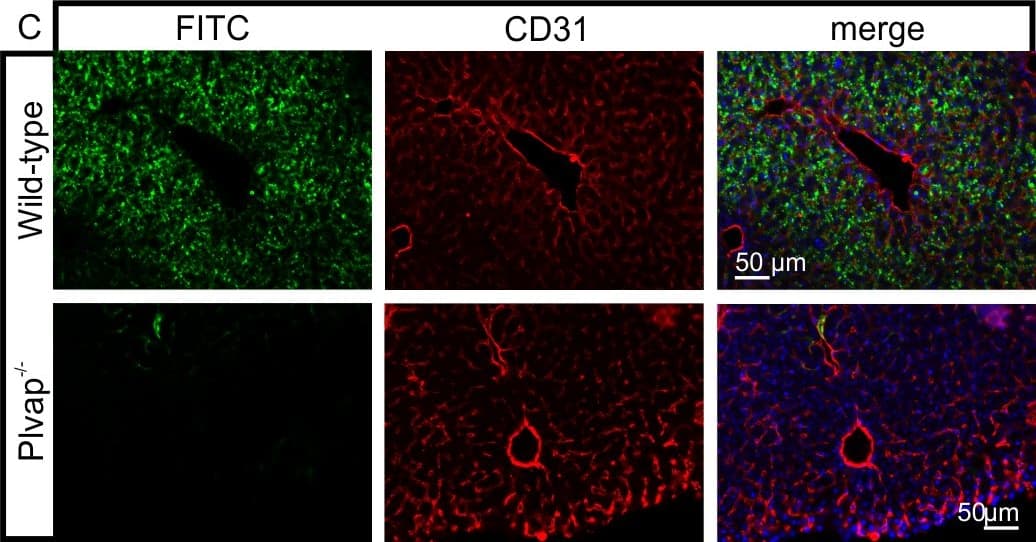
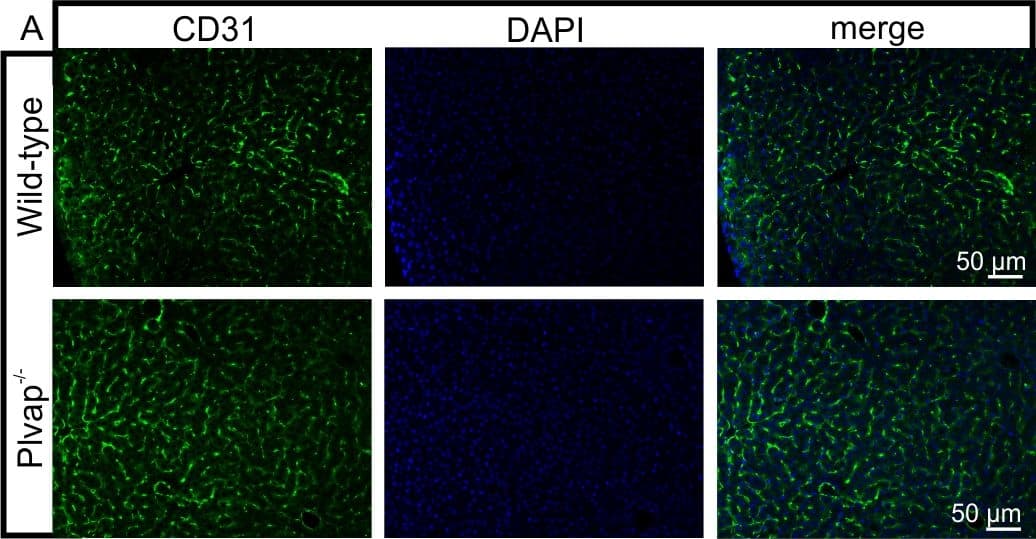
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Diminished permeability of liver sinusoids in Plvap-deficient mice.Neither by immunohistochemistry with antibodies against CD31 (A) nor by light microscopy of 1 µm semi-thin sections (B, Richardson's stain) obvious differences are detected with regards to the overall orientation and the density of liver sinusoids between 3-week-old Plvap-/- mice and wild-type littermates. Sinusoids of Plvap-deficient mice show a higher number of macrophages in their lumen (white arrows) and focal areas with accumulations of mononuclear cells in Disse's space (black arrows). Lower panels in B show higher magnifications. C, After perfusion of a wild-type animal with FITC-dextran, a strong FITC-signal (green) throughout the liver is detected. Immunolabeling with CD31 (red) suggests that FITC-dextran molecules have accumulated in the space of Disse. In contrast, in the Plvap-deficient littermate, the signal for FITC-dextran is much weaker and barely detectable. Nuclear DNA is labeled with DAPI (blue). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115005), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
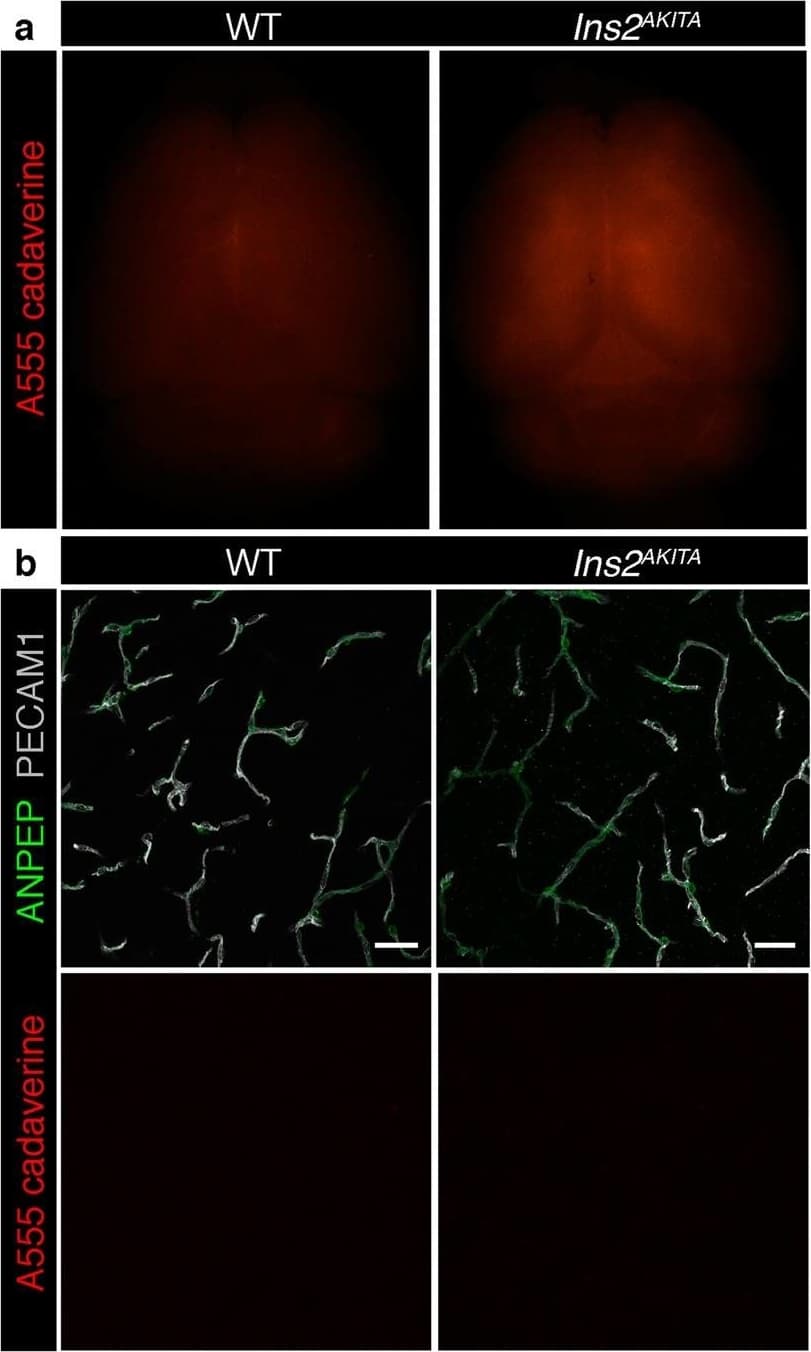
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunohistochemistry Blood-brain barrier permeability measurements in male Ins2AKITA and WT littermate controls. (a) Representative stereomicroscope fluorescence images of brains showing 1 kDa Alexa Fluor 555 cadaverine permeability in Ins2AKITA and WT after 2 h of dye circulation (n = 2). (b) Representative confocal images of coronal sections of 1 kDa Alexa Fluor 555 cadaverine injected mouse brains. ANPEP positive mural cells, green; PECAM1 positive vasculature, white. No Alexa Fluor 555 cadaverine leakage into brain parenchyma was observed either in Ins2AKITA or WT mice (n = 2, scale bar 30 μm). (c) Quantification of 1 kDa Alexa Fluor 555 cadaverine permeability in 26.5–32 week-old Ins2AKITA and WT mice after 2 h circulation (n = > 8, 3 independent experiments). y-axis shows the fold change in relative fluorescence units (RFU) per gram of brain tissue in relation to WT. (d) Quantification of 1 kDa Alexa Fluor 488 cadaverine permeability in 38 week-old Ins2AKITA and WT mice after 2 h circulation (n = 3). y-axis shows the fold change in relative fluorescence units (RFU) per gram of brain tissue in relation to WT. (e) Evans Blue dye permeability in 30 week-old Ins2AKITA and WT littermate control mice after overnight circulation (n = > 2). y-axis shows optical density (OD) at 620 nm per gram of tissue. PdgfbRet/Ret served as positive control for tracer leakage into the brain parenchyma. n.s., not significant, student’s t test. Data is presented as mean ± SEM. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30498224), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Diminished permeability of liver sinusoids in Plvap-deficient mice.Neither by immunohistochemistry with antibodies against CD31 (A) nor by light microscopy of 1 µm semi-thin sections (B, Richardson's stain) obvious differences are detected with regards to the overall orientation and the density of liver sinusoids between 3-week-old Plvap-/- mice and wild-type littermates. Sinusoids of Plvap-deficient mice show a higher number of macrophages in their lumen (white arrows) and focal areas with accumulations of mononuclear cells in Disse's space (black arrows). Lower panels in B show higher magnifications. C, After perfusion of a wild-type animal with FITC-dextran, a strong FITC-signal (green) throughout the liver is detected. Immunolabeling with CD31 (red) suggests that FITC-dextran molecules have accumulated in the space of Disse. In contrast, in the Plvap-deficient littermate, the signal for FITC-dextran is much weaker and barely detectable. Nuclear DNA is labeled with DAPI (blue). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115005), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence AcSDKP inhibits TGF beta /smad signaling and EndMT and restores the FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 levels in diabetic hearts. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/FGFR1 and CD31/P-MAP4K4 in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 μm in each panel. The CD31 and FGFR1 double-labeled cells and the CD31 and P-MAP4K4 double-labeled cells in each visual field were assessed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. (b and c) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/ alpha -SMA, VE-cadherin /SM22 alpha and CD31/p-smad3 expression levels in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 μm in each panel. The CD31 and alpha -SMA double-labeled cells, the VE-cadherin and SM22 alpha double-labeled cells and the CD31 and p-smad3 double-labeled cells in each visual field were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. Four mice from each group were analyzed. (d) Western blot analysis of the FGFR1, P-MAP4K4, TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2 and TGF beta 3 levels in cardiac tissues. A representative blot from four independent experiments was shown. The densitometric analysis of western blot data was presented (n=4). The diabetic mice are abbreviated as DM in the figure Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28771231), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
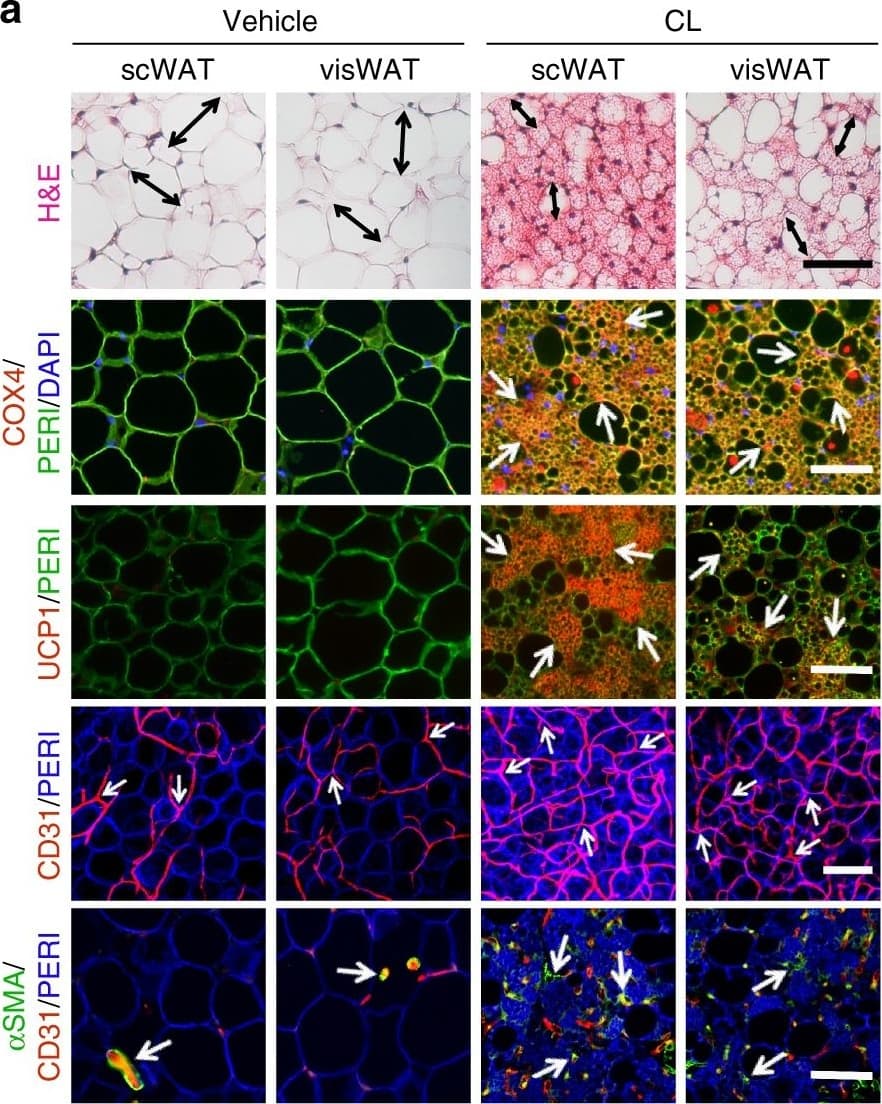
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence CL and low temperature lead to WAT browning, angiogenesis, and an increased number of myofibroblast-like cells. a, b Histological analysis of adipocyte morphology (H&E), adipocytes (PERI), mitochondria (COX4), uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), blood vessels (CD31), and myofibroblast-like cells ( alpha SMA) in a 5-day CL-316243-treated scWAT and visWAT compared to vehicle-treated control. b Two-week 4 °C-treated scWAT and visWAT compared to 30 °C control. Double-headed arrows mark adipocyte diameter. Arrows point to respective positive signals. c–l Quantifications of adipocyte size and positive signals per field of COX4, UCP1, CD31, and alpha SMA of CL-316243- and vehicle-, and 30 °C- and 4 °C- treated scWATs and visWATs (>30 adipocytes per field; n = 10 random fields; n = 5 mice per group). PERI, perilipin; COX4, mitochondrial complex 4; UCP1, uncoupling protein 1. Scale bars, 100 μm. NS, not significant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t-test. Data presented as mean ± s.e.m. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-02158-z), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
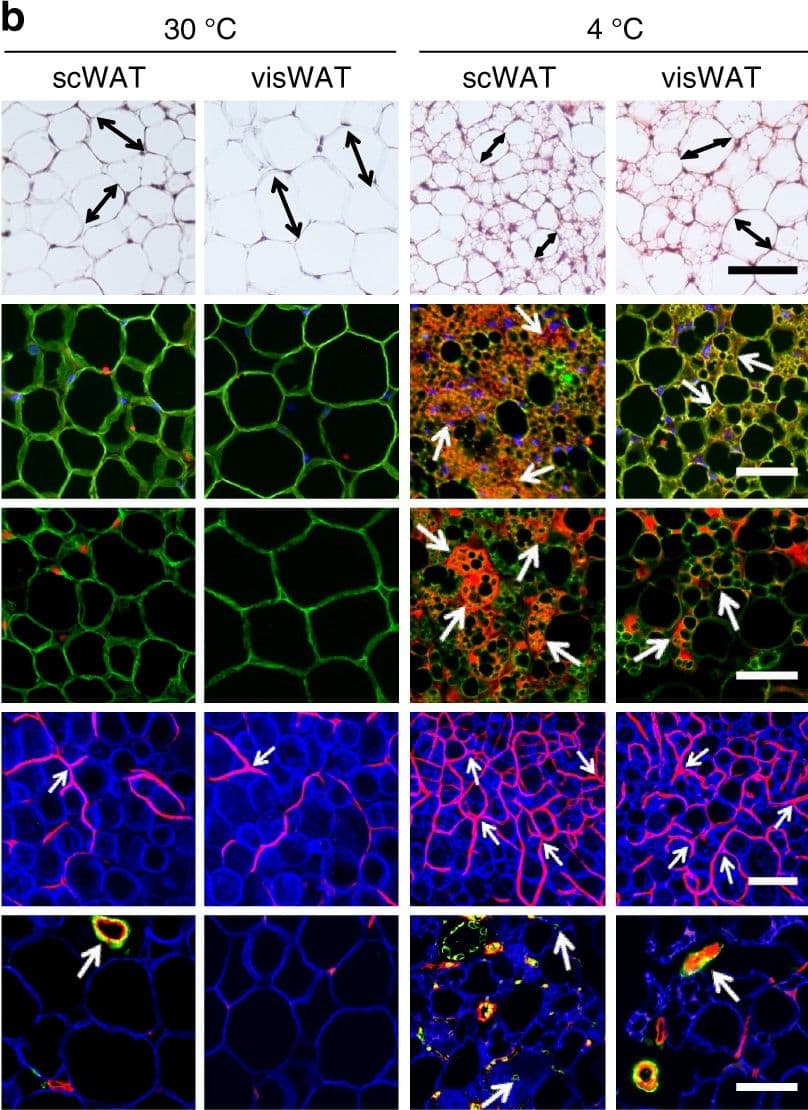
View LargerDetection of Mouse CD31/PECAM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence CL and low temperature lead to WAT browning, angiogenesis, and an increased number of myofibroblast-like cells. a, b Histological analysis of adipocyte morphology (H&E), adipocytes (PERI), mitochondria (COX4), uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), blood vessels (CD31), and myofibroblast-like cells ( alpha SMA) in a 5-day CL-316243-treated scWAT and visWAT compared to vehicle-treated control. b Two-week 4 °C-treated scWAT and visWAT compared to 30 °C control. Double-headed arrows mark adipocyte diameter. Arrows point to respective positive signals. c–l Quantifications of adipocyte size and positive signals per field of COX4, UCP1, CD31, and alpha SMA of CL-316243- and vehicle-, and 30 °C- and 4 °C- treated scWATs and visWATs (>30 adipocytes per field; n = 10 random fields; n = 5 mice per group). PERI, perilipin; COX4, mitochondrial complex 4; UCP1, uncoupling protein 1. Scale bars, 100 μm. NS, not significant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t-test. Data presented as mean ± s.e.m. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-02158-z), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Whole Blood Granulocytes by Flow Cytometry Whole blood granulocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram) followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0107). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
Human/Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM-1 Antibody Summary
Glu18-Lys590
Accession # Q08481
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Flow Cytometry(2.5 µg/106 cells)
Immunohistochemistry(5-15 µg/mL)


Background: CD31/PECAM-1
PECAM-1 (Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1), also known as CD31, is a 130 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein adhesion molecule in the immunoglobulin superfamily (1, 2). Expression is restricted to cells involved in circulation, especially endothelial cells, platelets, monocytes, neutrophils and lymphocyte subsets. PECAM-1 is concentrated at cell-cell junctions and is required for Transendothelial Migration (TEM) (1-3). The Extracellular Domain (ECD) of PECAM-1 has ten potential N-linked glycosylation sites and six C2-type Ig-like domains, the first of which is critical for adhesion and extravasation (3, 4). The cytoplasmic domain contains Immunoregulatory Tyrosine-based Inhibitory and Switch Motifs (ITIM, ITSM) that mediate both inhibition and activation via phosphotyrosine-mediated engagement of SH2-containing signaling molecules (1, 5). Metalloproteinase-mediated ectodomain shedding occurs during apoptosis (6) but increased serum PECAM-1 ectodomain in HIV and active multiple sclerosis occurs independent of apoptosis (7, 8). In humans, expression of six isoforms with exon deletions in the cytoplasmic domain is tissue- and stage-specific, but full-length PECAM-1 is predominant. A form lacking the ITSM predominates in mouse (9). Mouse PECAM-1 ECD shows 77%, 63%, 63%, 63%, and 61% amino acid (aa) identity with rat, human, canine, porcine, and bovine PECAM-1, respectively. PECAM-1 participates with other adhesion molecules in some functions, but is the critical molecule for TEM. Homotypic PECAM-1 adhesion in trans, combined with cycling of PECAM-1 to and from surface-connected endothelial cell vesicles, leads leukocytes across endothelial tight junctions (3, 10). Homotypic adhesion and signaling functions also strongly suppress mitochondria-dependent apoptosis (11). In platelets, PECAM-1 is necessary for limiting thrombus formation (12) and promoting integrin-mediated clot retraction and platelet spreading (13), but mechanisms for these phenomena are unclear. PECAM-/- mice are deficient in chemokine-mediated chemotaxis (14).
- Ilan, N. and J.A. Madri (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:515.
- Xie, Y. and W.A. Muller (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5569.
- Liao, F. et al. (1997) J. Exp. Med. 185:1349.
- Nakada, M.T. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 164:452.
- Chemnitz, J.M. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:945.
- Ilan, N. et al. (2001) FASEB J. 15:362.
- Eugenin, E.A. et al. (2006) J. Leukoc. Biol. 79:444.
- Losy, J. et al. (1999) J. Neuroimmunol. 99:169.
- Wang, Y. et al. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284:H1008.
- Mamdouh, Z. et al. (2003) Nature 421:748.
- Gao, C. et al. (2003) Blood 102:169.
- Falati, S. et al. (2006) Blood 107:535.
- Wee, J.L. and D.E. Jackson (2005) Blood 106:3816.
- Wu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:3484.


Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
参考图片
Detection of Mouse CD31/PECAM‑1 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for CD31/PECAM‑1 at approximately 130 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
Detection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Mouse splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity‑purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628, filled histogram) or control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0108).
Detection of CD31/PECAM‑1 in Rat Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Rat splenocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0108).
CD31/PECAM‑1 in Mouse Embryo. CD31/PECAM‑1 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (E13.5) using Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat CD31/PECAM‑1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3628) at 10 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (yellow; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to developing endothelium. View our protocol for Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.






 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)