产品介绍
产品信息
分子量
130

背景
背景
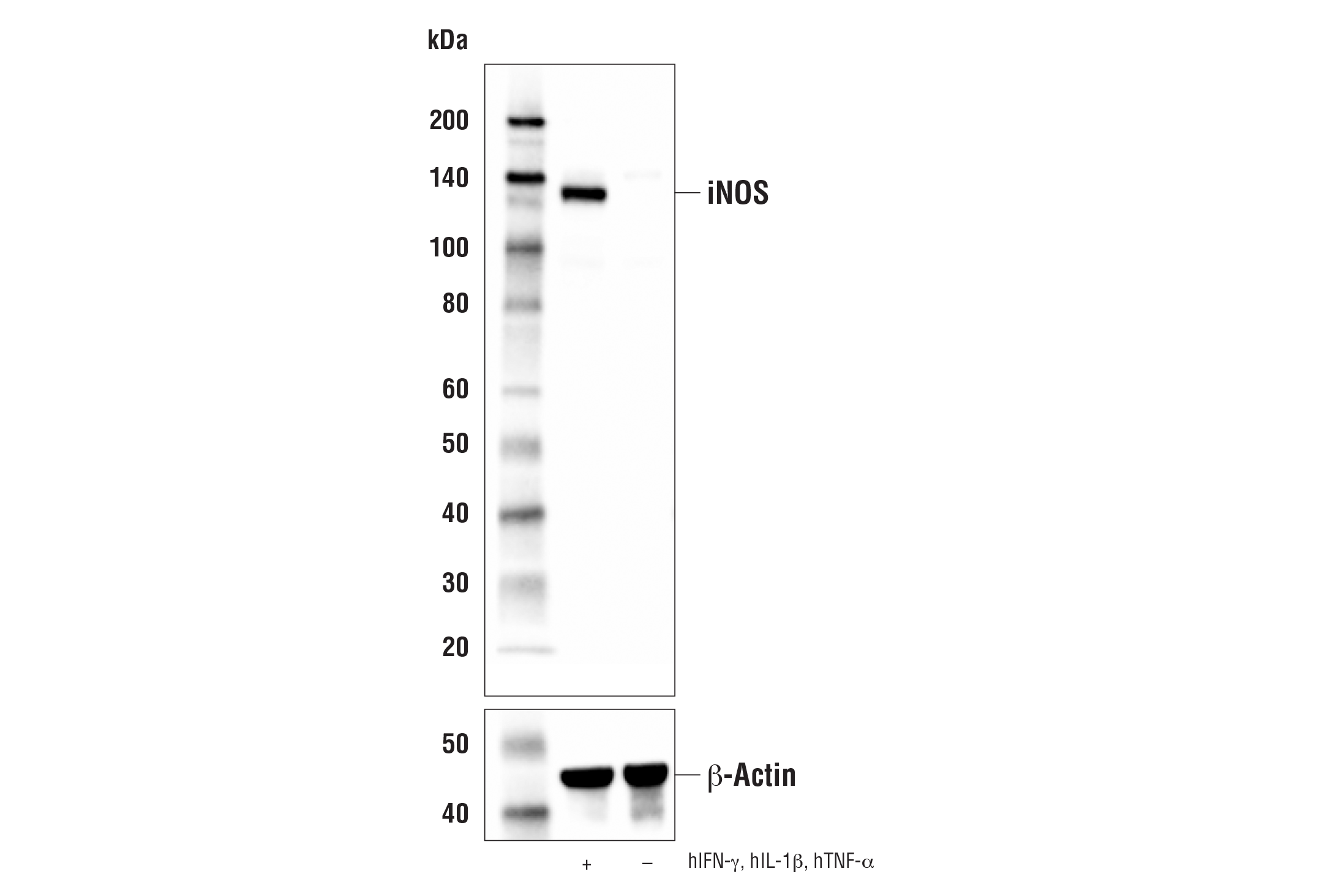
Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) catalyzes the formation of nitric oxide (NO) and citrulline from L-arginine, oxygen, and cofactors. Three family members have been characterized: neuronal NOS (nNOS), which is found primarily in neuronal tissue; inducible NOS (iNOS), which is induced by interferon gamma and lipopolysaccharides in the kidney and cardiovascular system; and endothelial NOS (eNOS), which is expressed in blood vessels (1). NO is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body, including the maintenance of vascular integrity, homeostasis, synaptic plasticity, long-term potentiation, learning, and memory (2,3).NO catalyzed by iNOS is involved in host defense against protozoa, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Unlike constitutively expressed eNOS and nNos, iNOS is not usually expressed in quiescent cells. iNOS is transcriptionally induced in response to bacterial endotoxins, such as LPS and proinflammatory cytokines, in macrophages and various other cell types. Transcription factors involved in iNOS transcription include NF-κB, AP-1, and STAT. Different signaling pathways either promote (Jak1/2, PKC, c-Raf, p38 MAP kinase, and p44/42 MAP kinase) or inhibit (PI3 kinase) iNOS expression depending on stimulus and cell type (4).
1.Tsutsui, M. (2004) J Atheroscler Thromb 11, 41-8.
2.Son, H. et al. (1996) Cell 87, 1015-23.
3.Hawkins, R.D. (1996) Neuron 16, 465-7.
4.Bogdan, C. (2001) Nat Immunol 2, 907-16.

研究领域
癌症,代谢,神经科学
声明 :本官网所有报价均为常温或者蓝冰运输价格,如有产品需要干冰运输,需另外加收干冰运输费。








 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷







 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)