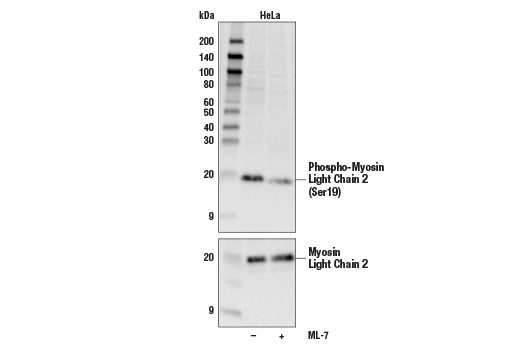



Myosin is composed of six polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two pairs of light chains. Myosin light chain 2 (MLC2), also known as myosin regulatory light chain (MRLC), RLC, or LC20, has many isoforms depending on its distribution. In smooth muscle, MLC2 is phosphorylated at Thr18 and Ser19 by myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) in a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent manner (1). This phosphorylation is correlated with myosin ATPase activity and smooth muscle contraction (2). ROCK also phosphorylates Ser19 of smooth muscle MLC2, which regulates the assembly of stress fibers (3). Phosphorylation of smooth muscle MLC2 at Ser1/Ser2 and Ser9 by PKC and cdc2 has been reported to inhibit myosin ATPase activity (4,5). Phosphorylation by cdc2 controls the timing of cytokinesis (5). Transgenic mice lacking phosphorylation sites on the cardiac muscle isoform show morphological and functional abnormalities (6). 1.Ikebe, M. and Hartshorne, D.J. (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 260, 10027-10031. 2.Tan, J. L. et al. (1992) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 721-759. 3.Totsukawa, G. et al. (2000) J. Cell Biol. 150, 797-806. 4.Ikebe, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 262, 9569-9573. 5.Satterwhite, L. L. et al. (1992) J. Cell Biol. 118, 595-605. 6.Sanbe, A. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21085-21094.







 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷







 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)