

1/6
产品介绍
产品信息
产品详情
Chromatin Regulation / Nuclear Function
简单描述
Sonication ChIP kit for both cells and tissues. Specially formulated cell and nuclear lysis buffers help protect chromatin integrity and antibody epitopes.

组合货号
57976S&76155S

组成成分
蛋白酶K,IgG 抗体,核酸外切酶,丙三醇 (甘油),迭氮(化)钠,水

应用
实验应用
CHIP

目标/特异性
Specificity/Sensitivity
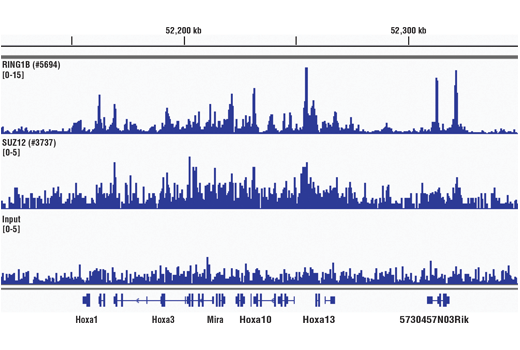
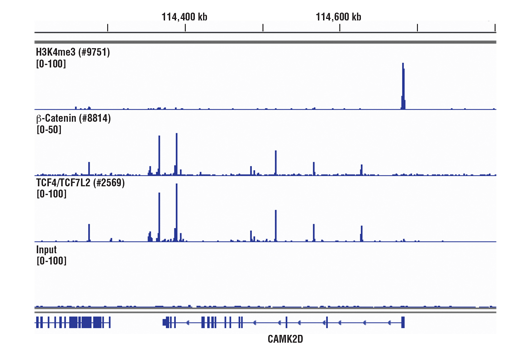
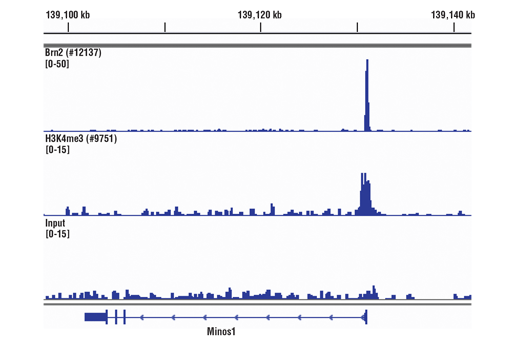
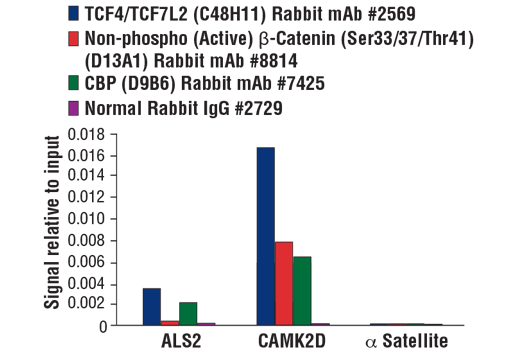
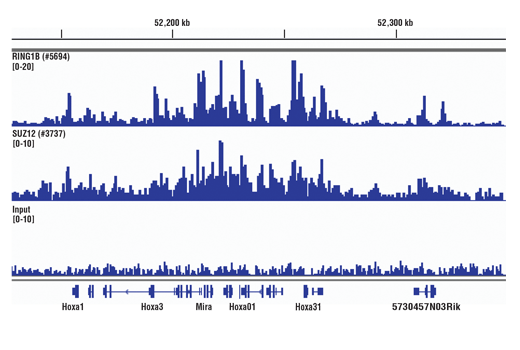
The SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit can be utilized with ChIP-validated antibodies to detect endogenous levels of protein-DNA interactions and histone modifications in mammalian cells and tissue samples (see Figures 1 to 4). The cell and nuclear lysis buffers for this kit have been optimized to maximize enrichment of chromatin containing histones, transcription factors and cofactors. The positive control Histone H3 Antibody recognizes many different species of the highly conserved Histone H3 protein, including human, mouse, rat and monkey. Primer sets are included for the human and mouse positive control RPL30 gene loci; however, the use of other species with the kit requires the design of additional control primer sets.

背景
背景
The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is a powerful and versatile technique used for probing protein-DNA interactions within the natural chromatin context of the cell (1,2). This assay can be used to identify multiple proteins associated with a specific region of the genome, or the opposite, to identify the many regions of the genome bound by a particular protein (3-6). It can be used to determine the specific order of recruitment of various proteins to a gene promoter or to "measure" the relative amount of a particular histone modification across an entire gene locus (3,4). In addition to histone proteins, the ChIP assay can be used to analyze binding of transcription factors and co-factors, DNA replication factors and DNA repair proteins. When performing the ChIP assay, cells or tissues are first fixed with formaldehyde, a reversible protein-DNA cross-linking agent that "preserves" the protein-DNA interactions occurring in the cell (1,2). Cells are lysed and chromatin is harvested and fragmented using either sonication or enzymatic digestion. The chromatin is then immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific to a particular protein or histone modification. Any DNA sequences that are associated with the protein or histone modification of interest will co-precipitate as part of the cross-linked chromatin complex and the relative amount of that DNA sequence will be enriched by the immunoselection process. After immunoprecipitation, the protein-DNA cross-links are reversed and the DNA is purified. Standard PCR or Quantitative Real-Time PCR can be used to measure the amount of enrichment of a particular DNA sequence by a protein-specific immunoprecipitation (1,2). Alternatively, the ChIP assay can be combined with genomic tiling micro-array (ChIP on chip) techniques, high throughput sequencing, or cloning strategies, all of which allow for genome-wide analysis of protein-DNA interactions and histone modifications (5-8).
1.Orlando, V. (2000) Trends Biochem Sci 25, 99-104.
2.Liu, Q. et al. (2000) Genes Dev 14, 1448-59.
3.Kuo, M.H. and Allis, C.D. (1999) Methods 19, 425-33.
4.Zhao, H. and Piwnica-Worms, H. (2001) Mol Cell Biol 21, 4129-39.
5.Agalioti, T. et al. (2000) Cell 103, 667-78.
6.Jiang, K. et al. (2003) J Biol Chem 278, 25207-17.
7.Soutoglou, E. and Talianidis, I. (2002) Science 295, 1901-4.
8.Martin, S.A. and Ouchi, T. (2008) Mol Cancer Ther 7, 2509-16.
9.Mikkelsen, T.S. et al. (2007) Nature 448, 553-60.
10.Chen, M.S. et al. (2003) Mol Cell Biol 23, 7488-97.
11.Lee, T.I. et al. (2006) Cell 125, 301-13.
12.Zeng, Y. et al. (1998) Nature 395, 507-10.
13.Weinmann, A.S. and Farnham, P.J. (2002) Methods 26, 37-47.
14.Löffler, H. et al. (2006) Cell Cycle 5, 2543-7.
15.Wells, J. and Farnham, P.J. (2002) Methods 26, 48-56.
16.Zachos, G. et al. (2007) Dev Cell 12, 247-60.
17.Garber, K. (2005) J Natl Cancer Inst 97, 1026-8.

制备和贮存
保存方式
All components in this kit are stable for at least 12 months past the reference date indicated on the component label when stored at the recommended temperature and left unused.
参考图片
声明 :本官网所有报价均为常温或者蓝冰运输价格,如有产品需要干冰运输,需另外加收干冰运输费。







 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷







 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)