


 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
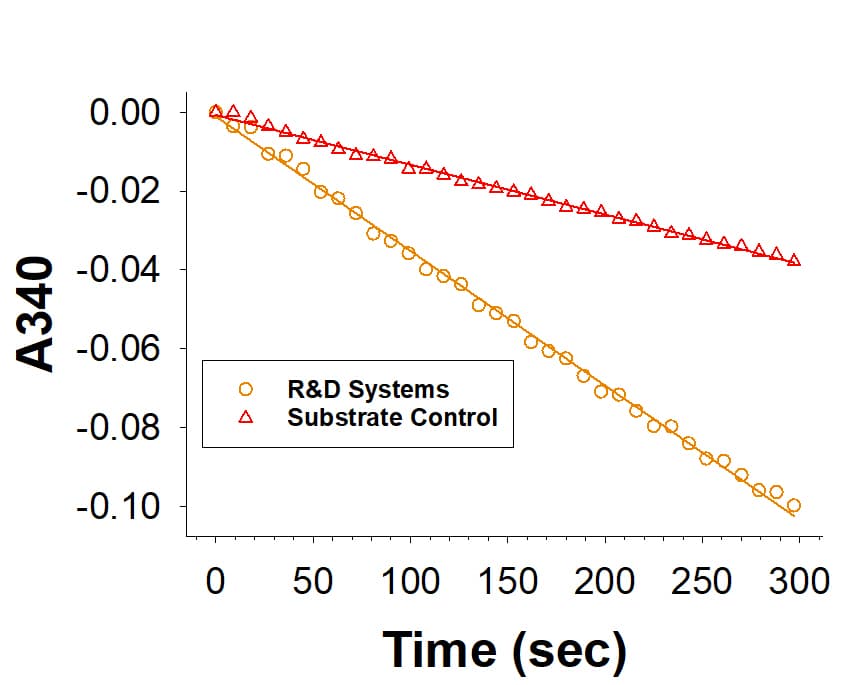
View LargerRecombinant Human SPR His-tag Protein (Catalog # 10209-SP) is measured by its ability to catalyze the reduction of phenanthrenequinone.
 View Larger
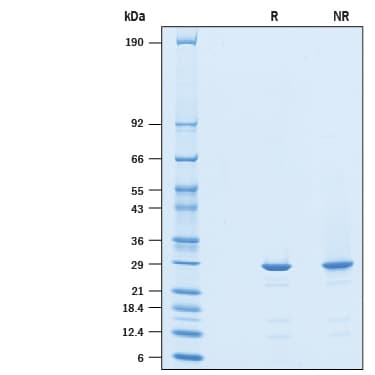
View Larger2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human SPR His-tag was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing a band at 28 kDa under reducing conditions.
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
10209-SP
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Human SPR His-tag Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Met1-Lys261
with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Analysis

Background: SPR
Sepiapterin reductase (SPR) catalyzes the biosynthesis of tetra-hydrobiopterin (BH4), an important cofactor in aromatic amino acid metabolism and key regulator of nitric oxide biosynthesis which relates the BH4 cofactor to many pathophysiological processes (1, 2). SPR has additionally been shown to be efficient at mediating chemical redox cycling of quinones and herbicides through a mechanism distinct from sepiapterin reduction (3). SPR is an NADPH-dependent, cytoplasmic enzyme classified as a member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) family based on its structural catalytic domain and NADPH binding motifs (4). SPR forms an active homodimer where each monomer contains a key c-terminal asparagine required for activity (3) in addition to the conserved catalytic triad that serves to stabilize protein structure while maintaining cofactor and substrate proximity in a catalytic site composed of several hydrophobic amino acids (4-6). SPR contains the conserved NADPH binding motif at the N-terminus (4-6). SPR has broad tissue expression (7). Identified human mutations in SPR result in compromised production of biopterin cofactor and are associated with neurological deficits (8, 9) linked to dystonia (8, 10). Knockout in mice likewise results in reduced neurotransmitters and movement disorders (11). Loss of BH4 can also reduce nitric oxide production leading to alterations in cardiac function and inflammation (2). SPR has been pharmacologically targeted to reduce pathologically elevated BH4 for pain management (12, 13) and to regulate T-cell function in pathological diseases and tumor growth (14).
- Werner, E.R. et al. (2011) Biochem. J 348:397.
- Bendall, J. K. et al. (2014) Antiox. Redox. Signal 20:3040.
- Yang, S. et al. (2013) J. Biol. Chem. 288:19222.
- Jornvall, H. et al. (1995) Biochemistry 34:6003.
- Auerbach, G. et al. (1997) EMBO J. 16:7219.
- Fujimoto, K. et al. (2001) Chem. Biol. Interact. 130:825.
- Katoh, S. (1971) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 146:202.
- Bonafe, L. et al. (2001) Am. J. Hum. Genet 69:269.
- Farrugia, R. et al. (2007) Mol. Genet. Metab. 90:277.
- Abeling, N.G. et al. (2006) Mol. Genet. Metab. 89:116.
- Yang, S. et al. (2006) Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78:575.
- Latremoliere, A. et al. (2015) Neuron. 86:1393.
- Fujita, M. et al. (2019) Arthritis Rheumatol. [Epub ahead of print]
- Cronin, S.J.F. et al. (2018) Nature. 563:7732.





 危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)
危险品化学品经营许可证(不带存储) 许可证编号:沪(杨)应急管危经许[2022]202944(QY)  营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)