视频素材来源于YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=paw2SUY22_s
版权归原作者所有
程序性细胞死亡早期的特征是线粒体功能的破坏。
线粒体破坏包括膜电位的变化,线粒体健康的主要特征以及线粒体氧化还原电位的改变。
内线粒体膜电位在Ca2+的吸收和储存,活性氧的产生和排毒以及最重要的是通过氧化磷酸化合成ATP方面至关重要。
可以使用多种基于荧光的分析方法检测线粒体功能的破坏,包括测量线粒体钙,超氧化物,线粒体通透性转变和膜电位。

△点击放大图片
实验步骤
- 1
- 2
- 3
-
实验方法一: JC-1线粒体膜电位检测
质子泵存在于线粒体内膜,可将基质内质子泵入膜间隙,质子跨膜转运使得线粒体膜间隙积累大量质子,形成质子梯度:线粒体膜间隙产生大量正电荷,而线粒体基质产生大量负电荷,从而形成跨线粒体内膜的跨膜电位(ΔΨ),简称为线粒体膜电位。
正常线粒体膜电位是维持线粒体进行氧化磷酸化、产生ATP的前提,是维持线粒体功能所必需,而凋亡过程中一个重要的变化即是线粒体膜电位的崩溃。
△点击放大图片
JC-1是亲脂性阳离子荧光染料可结合到线粒体基质,其荧光的增强或减弱说明线粒体内膜电负性的增高或降低。
1、 正常生理状态下,线粒体负电性高,JC-1进入线粒体以多聚体(Aggregates)存在,FL2 channel可观察到红色荧光。
2、 细胞走向凋亡时,线粒体去极化产生,负电性降低,JC-1则以单体(Monomer)存在在细胞质,在FL1 channel可以观察到绿色荧光增加。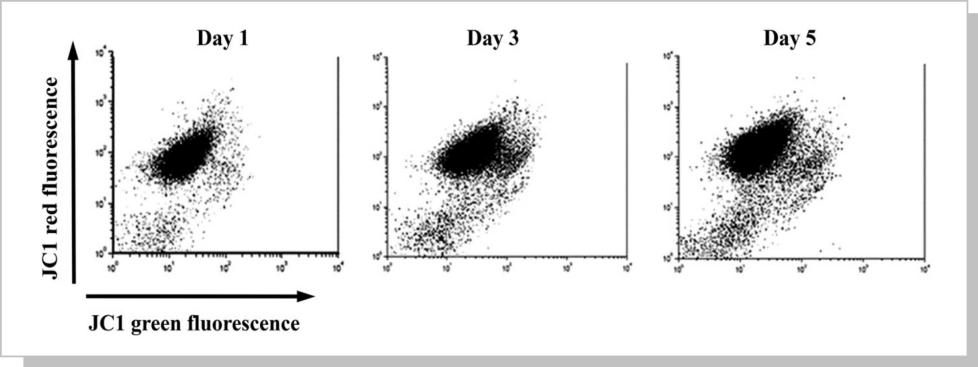
△点击放大图片
实验案例结果说明:Decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) during storage is evidenced with JC-1 analysis. Displacement of the platelet population from FL-2 channel to FL-1 channel supports the decline in ΔΨm over time. An increase in unstained platelets in the inferior left region indicates the formation of platelet microparticles.
-
实验方法二: 凋亡中线粒体的重要蛋白检测

△点击放大图片
-
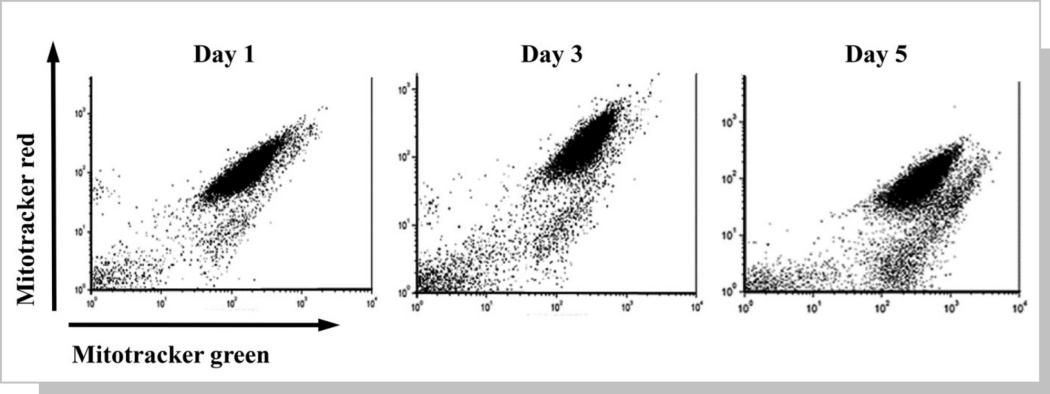
实验方法三: 线粒体膜电位的终点测定
△点击放大图片
△点击放大图片
实验案例结果说明: Decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and presence of platelet swelling during storage is evidenced with MitoTracker analysis on days 1, 3, and 5. Dislocation of the platelet population from FL-3 channel to FL-1 channel demonstrates the decline in ΔΨm along an increase in platelet swelling.

