实验步骤
- 1
- 2
-
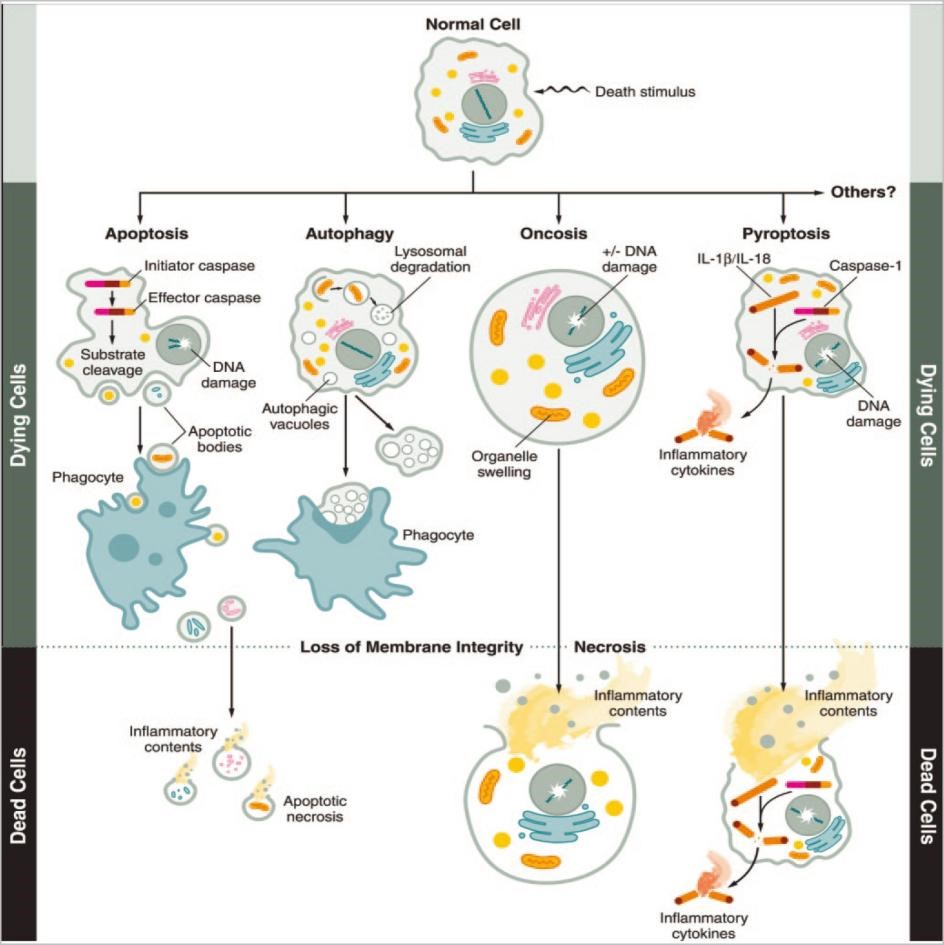
不同死亡形式的比较(形态、特征、检测方法、抑制剂)
死亡形式 特征 特点 检测方法 抑制剂 Apoptosis
淍亡
Cell shrinkage, cell membrane blebbing, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation. Almost all eukaryotic cells can undergo apoptosis and it involves caspase-activation via:
1. Extrinsic pathway induced by TNF, FAS, or TRAIL
2. Intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway mediated by proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins
3. ER stress pathway mediated by IRE1 and CHOPRequired for development.Maintenance of cell number.removal of damaged, infected,or stressedcells.Mayleadto degenerative diseases Annexin-V assay, electron microscopy, in situ end labelling (ISEL),immunoblotting,immunohistofluorescence,detection of ER stress markers by RT-PCR BAX inhibitor-1, BAX inhibiting peptide V5, BI-6C9, bongkrekicacid, NS3694, pifithrin-α Necrosis
坏死
Cell swelling andrupture,organelle damage, inflammation. Cells that are exposed to trauma, pathogens,nutrient starvation, ATP depletion, and mitochondrial permeability transition can undergo necrosis. Reported for most of the eukaryotic cells Can disrupt homeostasis, may lead to pathologicalconditions.Necrotic cells canelicitimmuneresponse BAX inhibitor-1, BAX inhibiting
peptide V5, BI-6C9, bongkrekicacid, NS3694, pifithrina Time-lapse microscopy, electron microscopy, hexosaminidase assay, calcein-AM release as-say.Geldanamycin, radicicol,cyclosporin A, JW47,sanglifehrinA Methuosis
巨泡式死亡
Large, fluid-filled cytoplasmic vac-oles formed due to suppressed recycling of macropinosomes,organelle swelling and rupture of the cell. Chiefly operated via Ras-Rac-1 signaling pathway.Reported in glioblastoma and gastric cancer cells Biological significance is not clear.Can be utilised therapeutically against apoptosis-resistant cells Geldanamycin, radicicol,cyclosporin A, JW47,sanglifehrinA Electron microscopy, time-lapse and fluorescence microscopy, visualisation of the vacuoles with fluorescent dves (LysoTracker, Lucifer yellow), metabolic flux analv-sis EHT 1864, bafilomycin A1 Necroptosis
坏死性
凋亡Cell membrane swelling and rupture. Displays features of both apoptosis and necrosis.
Operated by TNFR1-RIPK1/RIPK3 (necrosome)-MLKLpathway. Reported in many types of epithelial and cancer cellsStimulates inflammatory response,targeted necroptosis can impede cancer metastasis. Imaging flow cytometry,immunoblotting Necrostatin-1,necrosulfonamide,pazopanib, ponatinib NETosis
中性粒细胞外诱捕网死亡Disruption of the plasma membrane,decondensation of nuclear chromatin, the release of extracellular 'nets' comprising of chromatinfibresandmany cytosolic proteins.NADPH oxidase-and Ros--dependent.Characterised by histone citrullination by PAD4.Commonly seen in neutrophils Host defence against infection Light and electron microscopy,immunostaining, fluorescence microscopy, imaging flow cytometry, ELISA Staurosporine,diphenyliodonium,vanilloids Pyronecrosis
焦亡性细胞坏死Membrane rupture and cell lysis.Operated via an NLRP3- and cathepsin-dependent, caspase-independent, pathway. Commonly seen in monocytes,macrophages, and mast cells Plays a role in autoinflammatory diseases and host immune defence Flow cytometry,measurement of
IL-1B,ELISA,lactate dehydrogenase assay, electron microscopy, fluorescent microscopyCA-074Me, AMF1-5 Pyroptosis焦亡 Cell swelling, rupture of the cell membrane, and release of IL-1B.ASC-mediated inflammasome formation, followed by caspase-1-dependent activation of gasdermin D that create pores in cell membrane. Many types of eukaryotic cells undergopyroptosis Triggers inflammation,.Immune defenceagainstmicrobial intections Annexin-V and TUNEL assays,ELISA, lactate dehydrogenase assay, immunofluorescence,immunohistochemistry Necrosulfonamide, strychnine,brucine Autosis Focal enlargement of the perinuclear space, abundant autolysosomes and autophagosomes, swollen,electron-rich mitochondria, swol-len endoplasmic reticulum. Na*K'-ATPase pump plays a major role. Seen in many eukaryotic cells, including neurons and liver cells. Can be induced by Tat-beclin-1 peptide Can occur during cerebral hypoxia-ischemia and during an-orexianervosa Sytox Green staining, electron microscopy,immunofluorescence,immunohistochemistry,immunoblotting Neriifolin, digoxin, and digitoxigenin Entosis
细胞侵入
式凋亡Cellular cannibalism and the formation of cell-in-cell configu-ration. Induced by glucose star-vation. Assisted by E-cadherin.Facilitated by RhoA/ROCK1/2signalling pathway. Seen in can-cer cells including prostate cancer cells A survival response of the cells under glucosestarvation Immunoblotting,immunofluorescence,immunohistochemistry,AMPK-FRET measurements ROCKI/Il inhibitor (Y27632) cy.tochalasin B Ferroptosis铁凋亡 Iron-depend celldeath,initiated by lipid peroxides. Membrane rupture. Smaller mitochondria with the ruptured outer membrane. Signaling pathway involves AMPK-mediated phos-phorylation of beclin -1. Seen in many types of eukaryotic cells Suppression of tumorigenesis.May promoteneurodegenerative diseases Assessment of mitochondrial lipid peroxides Deferoxamine,desferrioxaminemesylate, ferrostatin-1,liproxstatin-1 Lysosomal membrane permeabilisation and Implicated in neurodegeneration,autoimmune diseases and cancer Electron microscopy,immunoblotting, cystatins, serpin Lysosome-dependent
cell death溶酶体依赖性细胞死亡translocation of cathepsins into the cytoplasm. Seen in many types of eukaryotic cells immunostaining, flow cytometry, Assessment of mitochondrial permeability transition ParthanatsPARP-1介导的程序性细胞死亡 Caspase-independent cell death induced by PARP-1 overactivation. Depolarised mito- chondrial membrane, DNA frag- mentation. Seen in several typeeukaryotic cells. Implicated in pathological conditions, such as Parkinson's
disease and strokeMeasurement of ROS immunofluorescence,annexin-V/PI staining,immunoblotting, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay INO-1001, benzamide,3-aminobenzamid, cilostazo -
几种死亡之形式比较铁死亡、凋亡、自噬
铁死亡
形态学特征
Small mitochondria with increasedmitochondrial membranedensities,reduction or vanishing ofmitochondria Crista, outer mitochondrial membrane Rupture and normal nucleus
生物学特征
Iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation
调控通路
Xc- /GPX4, MVA, sulfur transfer pathway, P62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway, P53/SLC7A11,ATG5-ATG7-NCOA4pathway,P53-SAT1-ALOX15pathway, HSPB1-TRF1,FSP1-COQ10-NAD(P)Hpathway
关键基因
GPX4, TFR1, SLC7A11, NRF2, NCOA4, P53,HSPB1, ACSL4, FSP1
检测指标阳性调控因子
ROS、PTGS2上升NADPH下降
阳性调控因子
Erastin、RSL3、RAS Sorafenib、p53
阴性调控因子
GPX4、FSP1、SLC7A11、NRF2、Ferrostatin-1、Liproxstatin-1、DFO
凋亡
形态学特征
Cellular and nuclear volume reduction, chromatin agglutination,nuclearfragmentation, formation of apoptotic bodiesand cytoskeletal disintegration, no significant changes in mitochondrial structure
生物学特征
DNA fragmentation
调控通路
Death receptor pathway, mitochondrionpathway and endoplasmic reticulum pathway;Caspase, P53, Bcl-2 mediated signaling pathway
关键基因
Caspase, Bcl-2, Bax, P53, Fas
检测指标阳性调控因子
细胞色素C释放caspase活化细胞内钙离子增高
阳性调控因子
p53、 Bax、Bak、TGF-B 地塞米松、放射线
阴性调控因子
Bcl-2、Bcd-XL Z-VAD-FMK、IL-4
自噬
形态学特征
Formation of double-mem braned autolysosomes, including macroautophagy, microautophagy and chaperone- mediated autophagy
生物学特征
Increased lysosomal activity
调控通路
mTOR, Beclin-1, P53 signaling pathway
关键基因
ATG5, ATG7, LC3, Beclin-1, DRAM3, TFEB
检测指标阳性调控因子
LC3-Ⅰ向LC3-Ⅱ转化
阳性调控因子
ATG家族、Beclin1
阴性调控因子
mTOR3-Methyladenine、Wortmannin、Spautin1